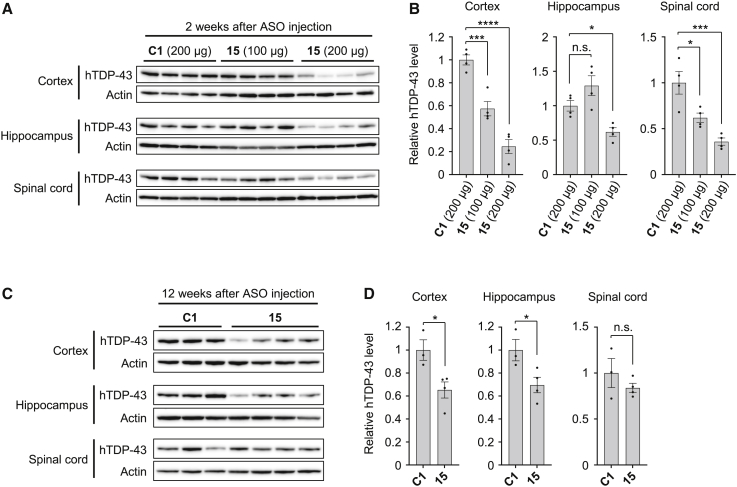
Figure 2.
Intracerebroventricular administration of gapmer ASO 15 decreases TDP43 protein levels in the brain and spinal cord of hTDP-43 mice
Western blot images (A and C) and bar graphs (B and D) showing relative hTDP-43 levels in hTDP-43 mice that were injected with either control ASO C1 (200 μg) or ASO 15 (100 or 200 μg in A and B; 200 μg in C and D) into the cerebral ventricles at 6 weeks of age. Protein levels of hTDP-43 in the cortex, hippocampus, and spinal cord were analyzed at 2 weeks (A and B) and 12 weeks (C and D) after ASO injection. Actin was used as a loading control. Data in (B) and (D) are presented as the mean ± SEM of 3–4 mice. Statistical analyses were performed to assess differences from the control group by one-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett multiple comparisons test in (B) and Student’s t test in (D). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant.