Figure 4.
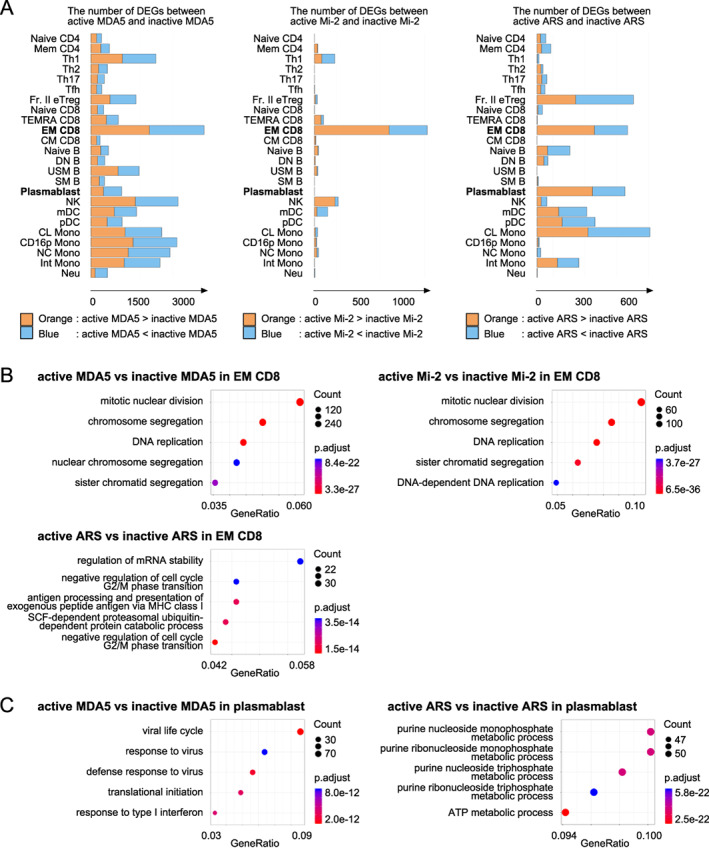
(A) Differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis between patients with active and patients with inactive idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) expressing each myositis‐specific antibody (MSA): antimelanoma differentiation associated gene 5 (MDA5) antibody (Ab) (left), anti‐Mi‐2 Ab (center), and anti‐aminoacyl‐transfer RNA synthetase (ARS) Ab (right). (B and C) Pathway analysis of DEGs in effecter memory CD8 (EM CD8) T cells and plasmablasts performed using ClusterProfiler. (B) Anti‐MDA5 Ab‐positive patients (upper left), anti‐Mi‐2 Ab‐positive patients (upper right), and anti‐ARS Ab‐positive patients (lower left) in EM CD8. (C) Anti‐MDA5 Ab‐positive patients (left) and anti‐ARS Ab‐positive patients (right) in plasmablasts. CL, classical; CM, central memory; CD16p, CD16 positive; DN B, double negative B; EM, effector memory; Fr. II eTreg, fraction II effector regulatory T; Int, intermediate; MDA5, melanoma differentiation‐associated gene 5; mDC, myeloid DC; NC, non‐classical; NK, natural killer; Neu, neutrophil; pDC, plasmacytoid DC; SM B, switched memory B; TEMRA, terminally differentiated effector memory; Tfh, follicular helper T; Th1, T helpler 1; USM B; unswitched memory B.
