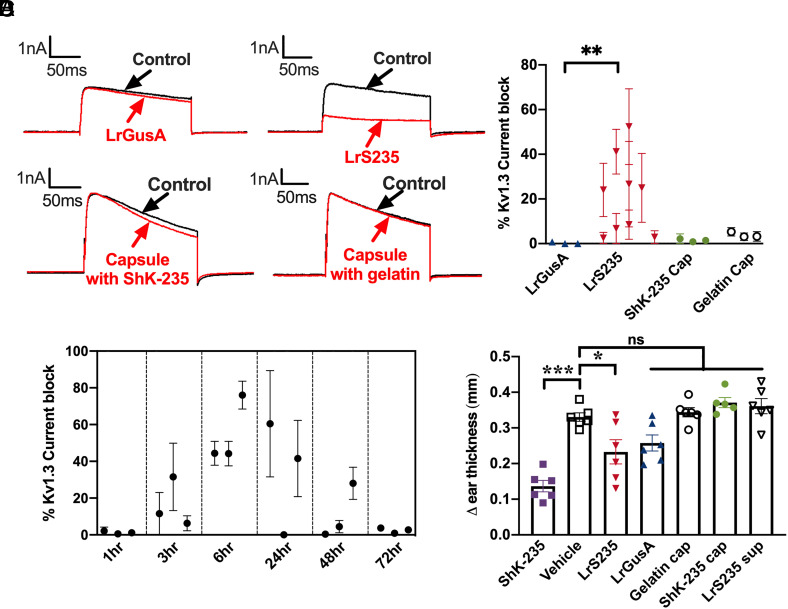
Fig. 2.
LrS235 secretes sufficient ShK-235 in the intestines for detection in the circulation of healthy rats. Healthy rats received an oral bolus of 1 × 109 cfu of LrGusA (▲) or LrS235 (▼), or an enteric-coated capsule filled with ShK-235 (●, 2 mg/kg body weight) or gelatin (o). Blood was drawn at different time points, and a single-cell patch-clamp was used to assess the ability of the serum to block Kv1.3 currents. A, Representative traces before (control) and after addition of serum diluted 1/100 from the 6-h time point. B, Current block of serum samples collected from rats at the 6-h time point. Each data point represents an individual rat. N = 3 to 4 measurements per rat. Serum dilution: 1/100. C, Current block of serum samples collected at the indicated time points. Each data point represents a rat. N = 3 to 4 measurements per rat. Serum dilution: 1/10. D, An active DTH reaction was induced against ovalbumin and rats received a single bolus of the following immediately before ear challenge: 1 × 109 cfu of LrGusA (▲) or LrS235 (▼) orally, an enteric-coated capsule filled with ShK-235 (●, 2 mg/kg body weight) or gelatin (o) orally, 1 mL of LrS235 culture supernatant orally (▽), or subcutaneous injection of 0.1 mg/kg synthetic ShK-235 (■) or vehicle (2). N = 6 rats per group (three males, three females). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.