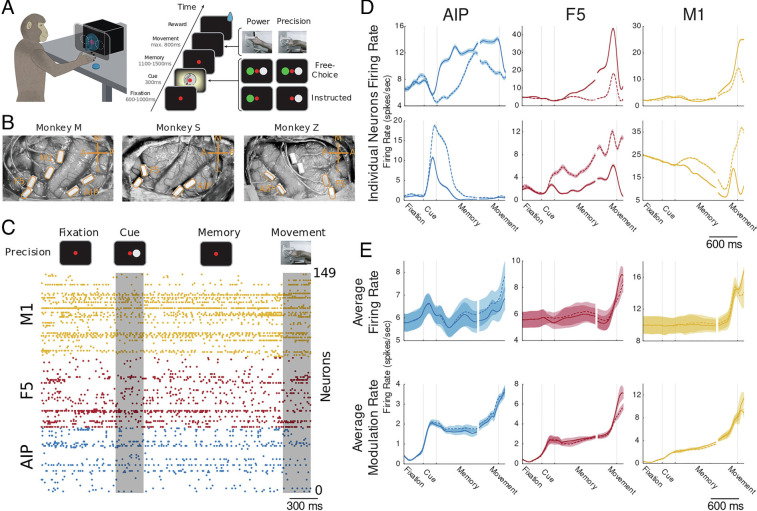
Fig. 3.
Behavioral task, electrode array implantation, and behavioral dependent firing rate modulations. (A) schematic view of the behavioral task is shown. Monkeys were placed in front of a grasping box with a masked monitor that was superimposed on the handle of the box. Monkeys were trained to execute one of two distinct grip types (precision grip or power grip) depending on the visual cue. Each trial of the task was initialized by the monkeys placing both hands on handrest buttons and fixating a red disc, followed by the cue epoch, in which one of the displayed cues was presented. After the cue offset, the monkeys had to continue fixing the red disc and prepare and memorize the appropriate movement. Finally, by turning off the red disc, monkeys were instructed to execute the appropriate grip type within a limited amount of time. (B) Surgical view of implanted floating microelectrode arrays in monkey M (Left), monkey Z (Middle), and monkey S (Right). Monkeys were implanted with two floating microprobe arrays per area (4 to 6 total, 32 electrodes each), in the cortical areas AIP, F5, and M1 of the frontoparietal grasping network. (C) Spike raster of all simultaneously recorded neurons of monkey M for one example precision condition trial. Spiking of all neurons is color-coded by area (M1 yellow, F5 red, and AIP blue). (D) Average firing rates of six representative neurons (two per area) over the time course of the task, separately for the two grasping conditions (solid line: precision condition; dashed line: power condition). Neurons in the Top row show stronger firing rates for the precision condition, whereas neurons in the Bottom row prefer the power condition. Shaded error bars represent SE across trials. (E) Top row: Average firing rate across all neurons for all recording sessions and monkeys separated by area and grip condition (solid line: precision condition; dashed line: power condition). Shaded error bars represent SE across recording sessions of all three monkeys. Bottom row: Same as in (D) but for average modulation rate. The modulation rate is the absolute difference in firing rate to baseline.