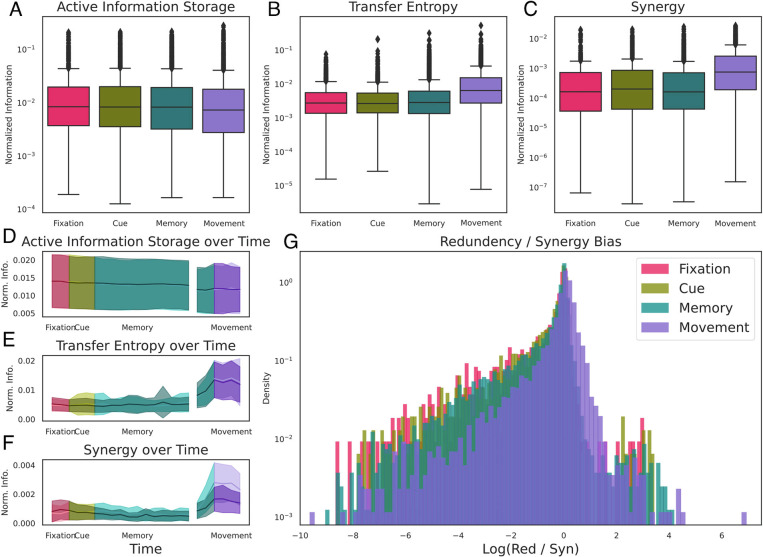
Fig. 4.
Behavioral state–dependent changes of information dynamics. All displayed information dynamics are averaged across all neurons of all three brain areas and the recording sessions of all three monkeys. (A–C) The differences in AIS (Left), mTE (Middle), and synergy (Right) between the four behavioral states of the task averaged across all sliding windows per task epoch and both conditions. There is no significant difference for AIS over time; however, mTE and synergy show increases during the movement epoch. (D–F) Time-resolved dynamics of AIS, mTE, and synergy over the time course of the task separately for the two grasping conditions (solid, power condition; shaded, precision condition). Shaded error bars represent SE across recording sessions of all three monkeys. Color-coded are the four behavioral epochs of the task (window contains 200 ms or more of the next epoch). (G) Distribution of synergy/redundancy bias across all significant effective neural connections for all four behavioral states, averaged across all sliding windows per task epoch. All states are, on average, synergy biased, even though the movement period is associated with a distinct increase in the proportion of redundant information.