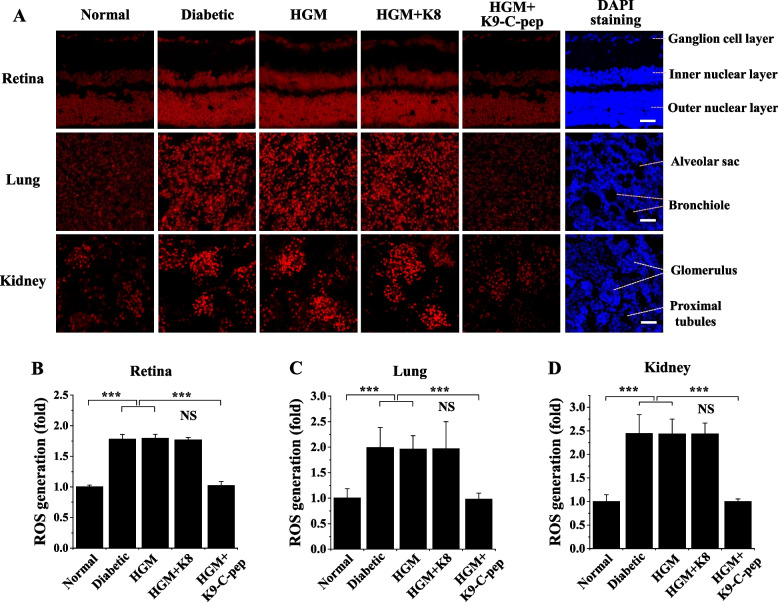
Fig. 2.
Systemic supplementation of human C-peptide via subcutaneous K9-C-peptide depots simultaneously inhibits HGM-induced ROS generation in the retinas, lungs, and kidneys of HGM mice. Six weeks after streptozotocin injection, C57BL/6 diabetic mice were treated for 4 weeks with insulin (HGM), insulin and K8 polypeptide (HGM + K8), or insulin and K9-C-peptide (HGM + K9-C-pep), as illustrated in Fig. 1A. Normal, non-supplemented diabetic, and HGM mice underwent sham operations as controls. ROS generation in the retina, lung, and kidney was visualized by confocal microscopy with dihydroethidium staining. A Representative fluorescence images of ROS generation. The nuclei were stained with DAPI to visualize cellular distribution in the sections. Scale bar, 50 µm. Quantification of ROS generation in the retina (B), lung (C), and kidney (D) sections by measuring the fluorescence intensity (n = 6). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. ***P < 0.001. NS, non-significant