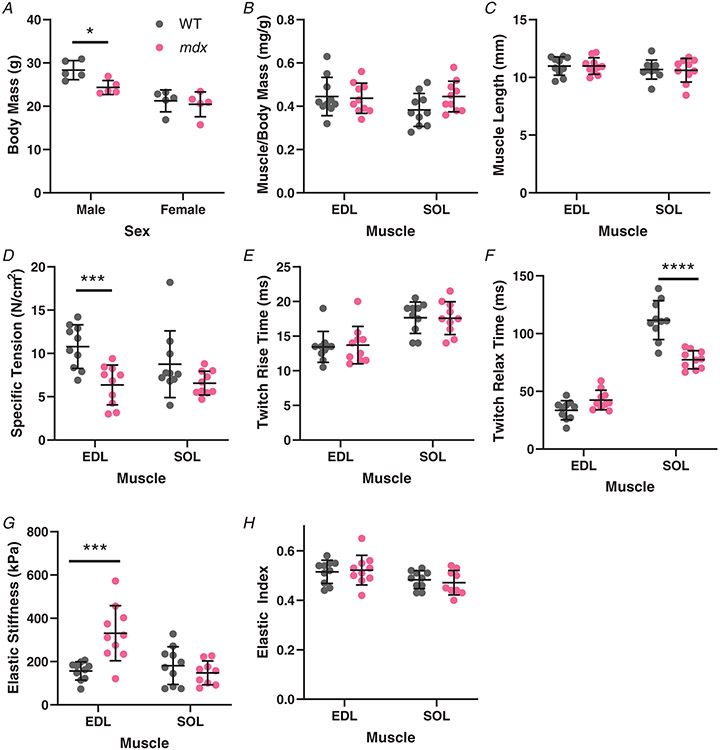
Figure 3. Muscle size and mechanical properties from wildtype (n = 10; 5M/5F) and mdx (n = 10; 5M/5F) mice.
A, total body mass was greater for male mice than female mice. Body mass of mdx males is significantly lower than wildtype males. B, the ratio of individual muscle masses to body mass is consistent across genotypes along with similar mass between EDL and soleus. C, muscle length (Lo) was set at the length of peak twitch force. Muscle length was consistent across all groups. D, the specific force of mdx EDL was significantly lower than wildtype, with a similar trend in soleus muscle that did not reach significance. E, twitch rise-time to half of active peak twitch tension is more rapid in the EDL muscle than soleus corresponding to the predominantly fast and slow phenotypes, respectively. The genotype had no impact on activation kinetics. F, there are genotype and muscle-specific impacts on relaxation time for twitch force to reach half of peak tension. The mdx EDL had little difference from wildtype EDL, while the mdx soleus relaxes more quickly than the wildtype soleus. G, elastic stiffness taken as the elastic modulus at 10% strain shows the mdx EDL is significantly stiffer than the wildtype EDL. The soleus had similar stiffness between genotypes. H, the elastic index, related to the amount of force remaining after stress relaxation compared with the peak force, showed no effect in mdx muscle. As a whole, the EDL muscles were significantly more elastic than soleus. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.