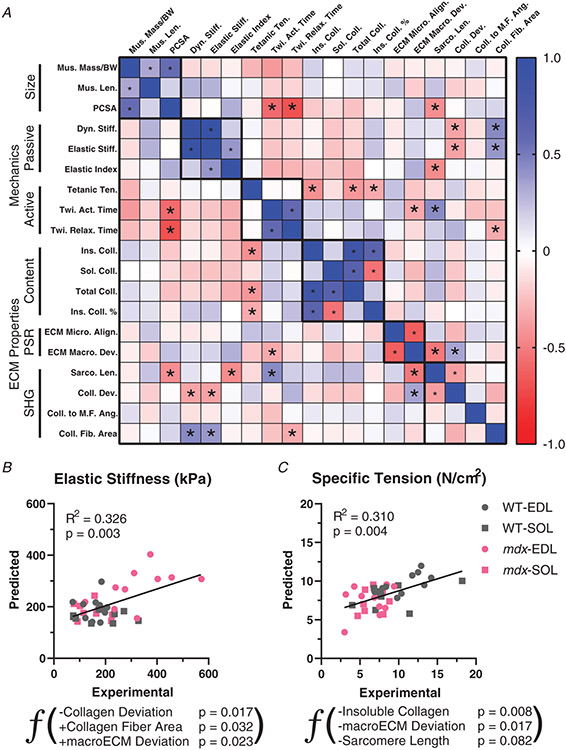
Figure 7. Relationships between muscle functional and ECM architectural parameters.
A, correlation matrix based on parameters of muscle size, active and passive mechanics, and ECM architecture determined by collagen content, polarized light and second harmonic generation (SHG). Blue indicates positive Pearson’s correlation coefficient values and red negative. *P < 0.05 indicates significant correlations. B, multiple linear regression analysis for elastic stiffness using ECM architectural properties as predictors. A negative relationship with collagen deviation was the most significant factor in the model. This is contrasted by a positive relationship with macroECM deviation. Higher collagen fibre area predicted greater elastic stiffness in the model. C, multiple linear regression analysis for specific tension using the same ECM architectural properties. Insoluble, i.e. crosslinked, collagen content was the most significant predictor of specific tension. The macroECM deviation had a negative relationship in the model, and sarcomere length was a modest negative predictor of specific tension.