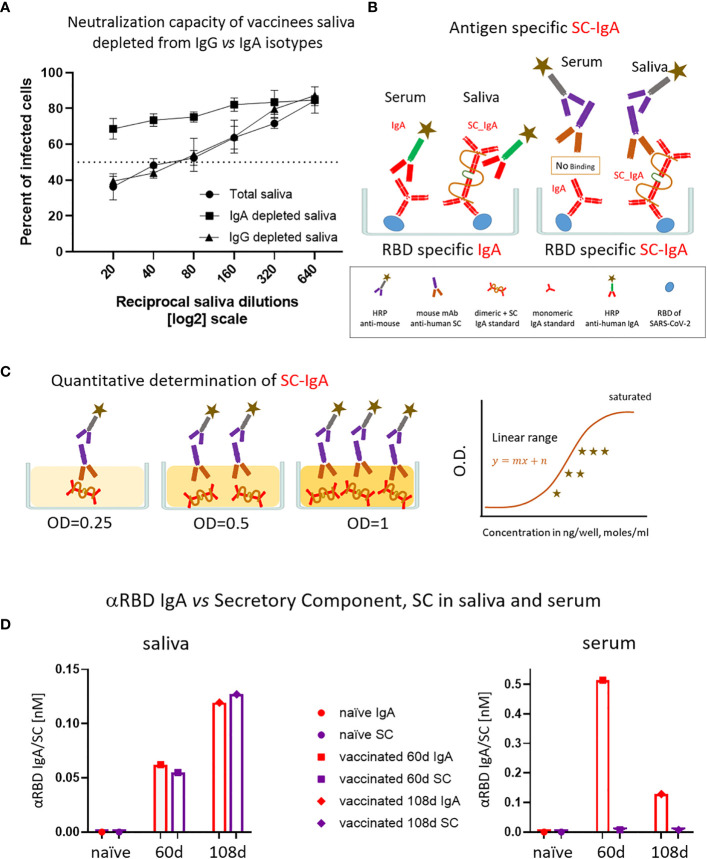
Figure 4.
The association of salivary anti-RBD IgA with the secretory component governs the prominent neutralization activity in vaccinees. (A) Depletion of IgA from saliva samples of vaccinees completely abrogates the specific neutralization activity of vaccinees saliva. Saliva neutralization was assessed by SARS-CoV-2 spike-pseudotyped VSV-GFP-ΔG reporter assay on Vero-E6 cells. The magnitude of neutralization is expressed as a percentage of pseudovirus-infected green cells without incubation with saliva (total infection = 100%). Percentage of measured neutralization by saliva pool of five vaccinees is plotted as a function of the reciprocal values of the saliva dilutions displayed on a log2 scale. The NT50 of saliva pool is reached on average at the dilution of ∼1:60 (extrapolated by the cross-section with the dashed line). Depletion of IgA results in abrogation of vaccine-induced neutralization activity (squares), whereas IgG-depleted saliva pool coincides with the non-depleted pool (triangles vs. circles). Depletion is achieved using anti-IgA and anti-IgG–specific magnetic beads. Results of three experimental repeats are represented. Analyses of completeness of isotype depletion and of its specificity are presented in Figure S4A . (B) Schematic outline of the detection of anti-RBD IgA in serum and SC-associated anti-RBD IgA in saliva samples. Illustrated are the expected differences between the circulatory monomeric IgA and the salivary mucosal dimeric/polymeric IgA, covalently bridged by J-chain and associated with pIgR. Left panel shows non-discriminative detection of both isoforms by anti-IgA secondary HRP-conjugate. Right panel shows the selective quantitative determination of dimeric/polymeric secretory IgA in saliva, but not in the serum, using anti-SC mouse monoclonal Ab, followed by anti-mouse secondary detection. (C) Molar quantification of dimeric secretory IgA. We introduce as reference standard using commercial secretory dimeric IgA purified from human colostrum to transform the OD values to their molar equivalents. We assume average molecular weight (MW) of dimeric secretory IgA = 424 g/mole. We considered IgA in its dimeric form because it is mostly found in that form at the mucosal surfaces and in mucosal secretions. (D) Analysis of dimeric anti-RBD SC-IgA in saliva (upper panel) vs. monomeric anti-RBD IgA in serum (lower panel) after vaccination, measured by quantitative ELISA. The molar expression in saliva is corrected to bi-valence to simplify the comparison to circulatory immunoglobulins.