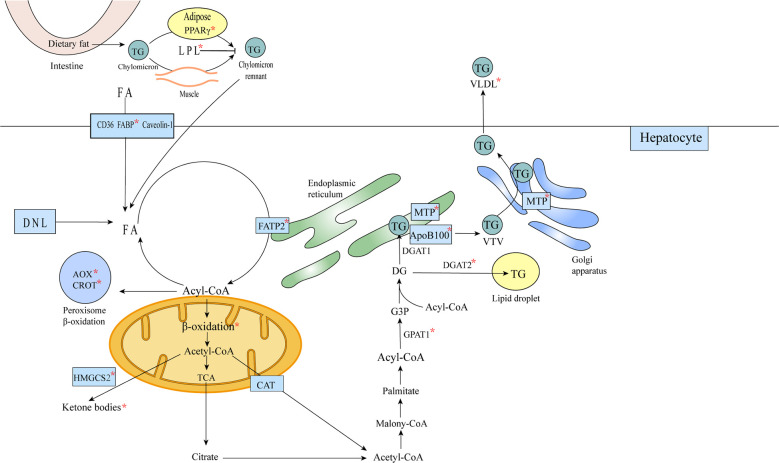
Figure 5.
FOXA affects lipid metabolism in hepatocytes. Triglycerides remaining in the chylomicron remnants are transported to the liver as a source of FA in hepatocytes, and FA translocase (FAT)/CD36, plasma membrane FA-binding protein (FABP) and Caveolin-1 mediate the uptake of fatty acids bound to circulating albumin, or the acquisition of FA through de novo lipogenesis (DNL). Acetyl coenzyme A is converted to citric acid, ketone bodies or to carnitine/acetyl coenzyme A (CAT), from the mitochondria into the cytosol (57). In the cytosol, acetyl coenzyme A is used for the synthesis of triglycerides and very low density lipoproteins. Triglycerides can be stored in intracellular lipid droplets or packaged into very low density lipoproteins and secreted into the plasma. The formation of mature VLDL requires two lipidation processes mediated by MTP (58).The metabolic processes or substances involved in metabolism affected by FOXA are marked with an asterisk in the figure.