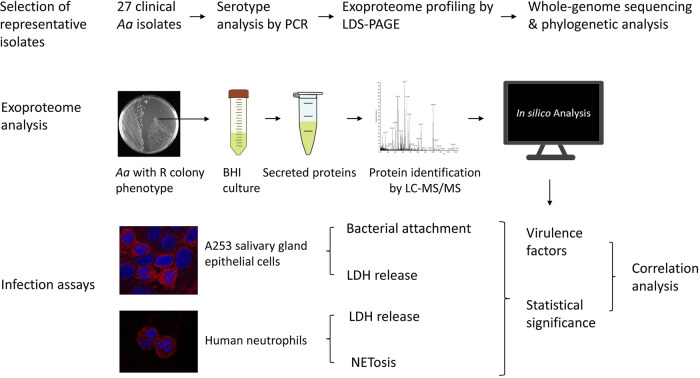
FIG 1.
Diagram of the study design. First, representative Aa isolates with serotypes a, b, or c were selected from a collection of 27 clinical isolates by PCR-based serotype identification and exoproteome profiling by LDS-PAGE. Genomes of 15 selected Aa isolates with serotypes a, b, or c were sequenced and their phylogenetic relationship was determined. Second, bacteria were transferred from a plate to BHI broth and, upon anaerobic standing culture, the secreted proteins were collected by centrifugation and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Third, the virulence of Aa isolates was assayed with A253 salivary gland epithelial cells and human neutrophils by determining attachment to epithelial cells, LDH release as a measure for cytotoxicity, and NETosis. Lastly, the production of virulence factors determined by MS was correlated with bacterial virulence in the different infection assays.