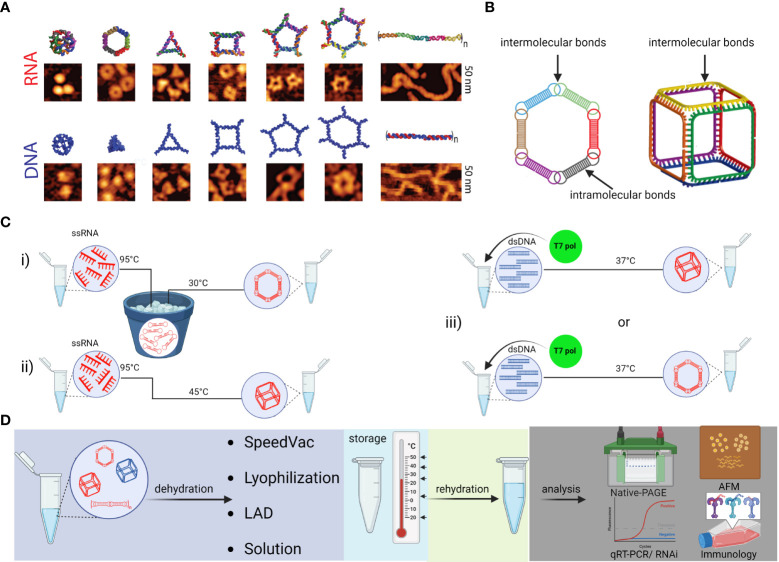
Figure 5.
Schematic depiction of various NANPs, their production, characterization, storage, and handling. (A) Computational 3D visualization of individual NANPs with corresponding representative AFM images. (B) Two orthogonal NANPs design strategies are based either on the presence of both intra- and intermolecular or only intermolecular bonds, which also determine the assembly protocol of corresponding NANPs. (C) Several protocols for efficient one-pot NANPs self-assembly. Protocol (i) promotes secondary structure formation of individual monomers needed for NANPs assembly via long-range interacting motifs. For this assembly protocol, the individual ssRNAs are first denatured by heating at 95°C and then snap cooled on ice to form intramolecular Watson-Crick (W-C) bonds. The following incubation at 30°C in the presence of Mg2+ ions allows intermolecular bindings of monomers and assembly of NANPs. In (ii)> protocol, monomers form only intermolecular canonical Watson-Crick base pairs, thus no pre-folding is needed, and any intramolecular interactions should be avoided by design. The (iii) protocol allows for co-transcriptional assembly of different types of NANPs formed as their RNA strands are transcribed from dsDNA templates. (D) Assembled NANPs can be stored and transported in anhydrous forms at ambient temperatures. The impact on structure stability, immunorecognition, and functionality depends of dehydration protocol and needs to be checked after rehydration for each type of NANP.