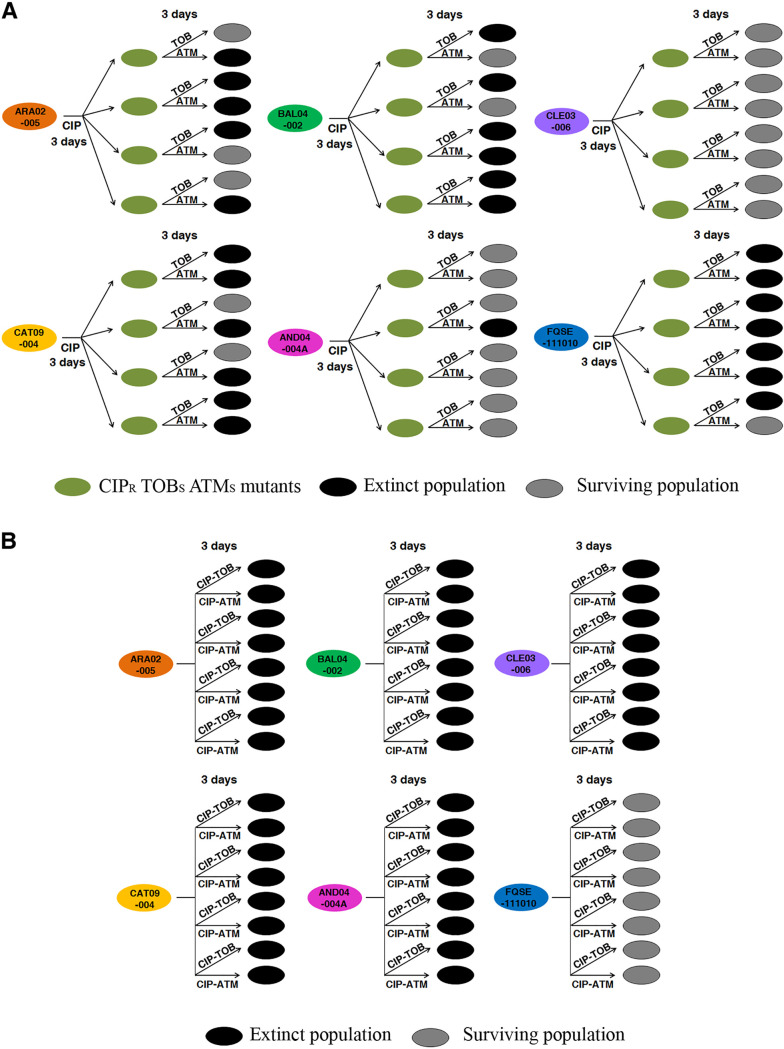
FIG 4.
Diagram showing alternation of ciprofloxacin with tobramycin or aztreonam and the combination of ciprofloxacin-tobramycin or ciprofloxacin-aztreonam to drive different antibiotic-resistant clinical strains of P. aeruginosa to extinction. (A) Short-term evolution was performed for 6 clinical isolates (FQSE11-1010, ARA02-005, BAL04-002, CLE03-006, CAT09-004, and AND04-004A), each represented as a cell with a different original color, with 4 replicate populations of each parental strain and for 6 days: 3 days in the presence of ciprofloxacin (or with the absence of antibiotic as a control), leading to ciprofloxacin-resistant populations (green cells), and 3 days in the presence of aztreonam or tobramycin. Extinct populations at the end of the experimental evolution are represented in black, while surviving populations are colored in gray. Thirteen and 12 out of 24 populations subjected to short-term ALE in the presence of tobramycin and aztreonam, respectively, became extinct after 3 days. This evolutionary strategy was ineffective in driving some replicate populations to extinction. (B) Short-term evolution of 6 clinical isolates (FQSE11-1010, ARA02-005, BAL04-002, CLE03-006, CAT09-004, and AND04-004A), represented as a cell with a different original color, with 4 replicate populations of each parental strain, was performed for 3 days in the presence of the ciprofloxacin-aztreonam and the ciprofloxacin-tobramycin combinations. Growth of the 72 control populations was confirmed for the 3 drugs independently used, at the same concentrations used for the drug combinations. Twenty out of 24 populations subjected to short-term ALE in the presence of each antibiotic combination became extinct. In all populations in which extinctions were observed, the differences with respect to the control were statistically significant (P < 0.001). These results indicate that CS may not only improve treatment when drugs are applied sequentially but also that this is even more useful to optimize combinatory therapy, including for the high-risk epidemic clones CAT09-004 and AND04-004A.