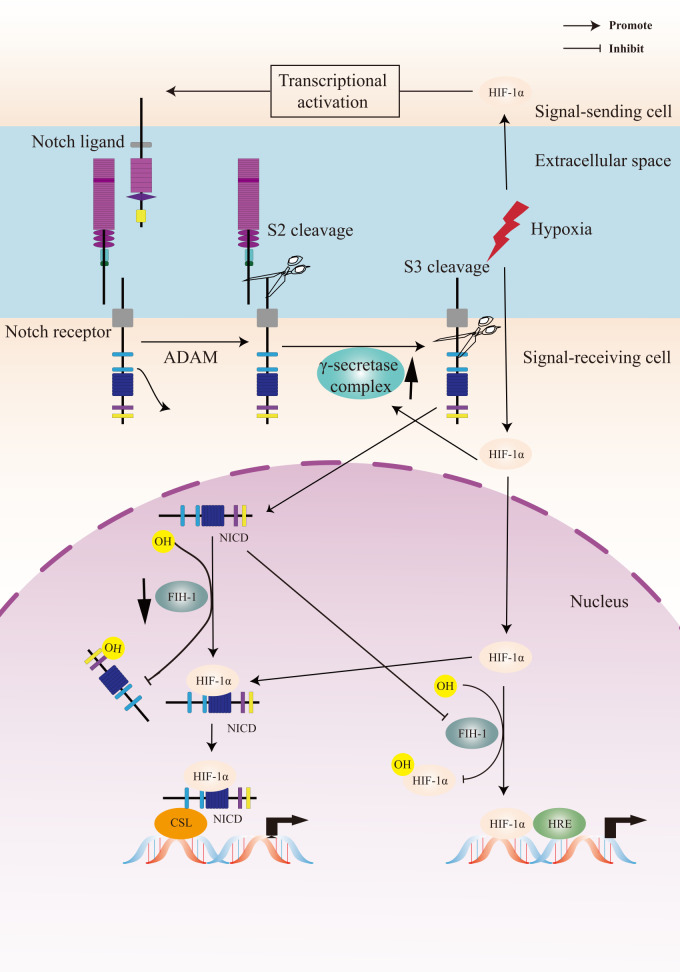
Figure 2.
A Crosstalk between Notch signaling and hypoxia pathway. Upon activation of the Notch receptor, the Notch intracellular domain (NICD) accumulates in the cell nucleus and activates target genes. Hypoxia induces the canonical hypoxia response pathway, which involves the activation of hypoxia response element (HRE)-driven target genes. Under hypoxic conditions, hypoxia-induced factors-1α (HIF-1α) potentiates Notch-dependent activation of target genes through interaction with the NICD. Besides, HIF-1α interacts with γ-secretase and upregulated γ-secretase activity. Factor-inhibiting HIF-1 (FIH-1) hydroxylates the asparagine residues of HIF-α and NICD, leading to inactivation of Notch and hypoxia signaling pathways. Hypoxia decreases the activity of FIH-1. In addition, FIH-1 binds NICD more efficiently than HIF-1α. NICD sequesters FIH-1 away from HIF-1α, indirectly resulting in an activation of HRE-driven target genes.