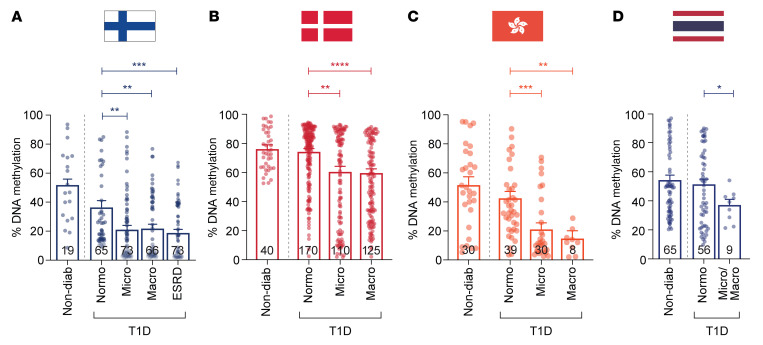
Figure 4. Validation of differentially methylated genes in replication cohorts.
(A) DNA methylation analysis of core genes was performed in a larger FinnDiane replication cohort (n = 296: 19 healthy, 65 Normo, 73 Micro, 66 Macro, and 73 ESRD) using a highly specific methyl-qPCR assay. Data show combined DNA methylation (%) for the 7 core genes: MTOR, RPTOR, IRS2 (insulin signaling), TXNRD1, LCAT, SMPD3 (lipid metabolism), and COL1A2 (integrin-cell interaction) using PCA loading analysis. Results show that reduced DNA methylation (%) is associated with DN. (B) Replication of FinnDiane-derived DDNs in samples from the Danish PROFIL study – Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen. Methyl-qPCR methylation analysis includes 40 nondiabetic and T1D individuals with Normo (n = 170), Micro (n = 110), and Macro (n = 125). (C) Methylation analysis of the DDNs in 77 age-matched T1D individuals from the Hong Kong T1D registry and 30 healthy controls. Individuals with T1D include 39 Normo, 30 Micro, and 8 Macro. (D) Methylation analysis of the DDNs in age-matched nondiabetic and T1D individuals recruited from the Theptarin registry, Thailand. DNA methylation (%) was assessed for genes in 65 controls and 65 cases (56 without renal complications and 9 with renal complications). Significance was calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test by comparing T1D with no complications (Normo) to Micro, Macro, and ESRD (A) or by comparing T1D with Normo and 9 T1D with Micro/Macro (combined) (B–D). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Error bars are SEM.