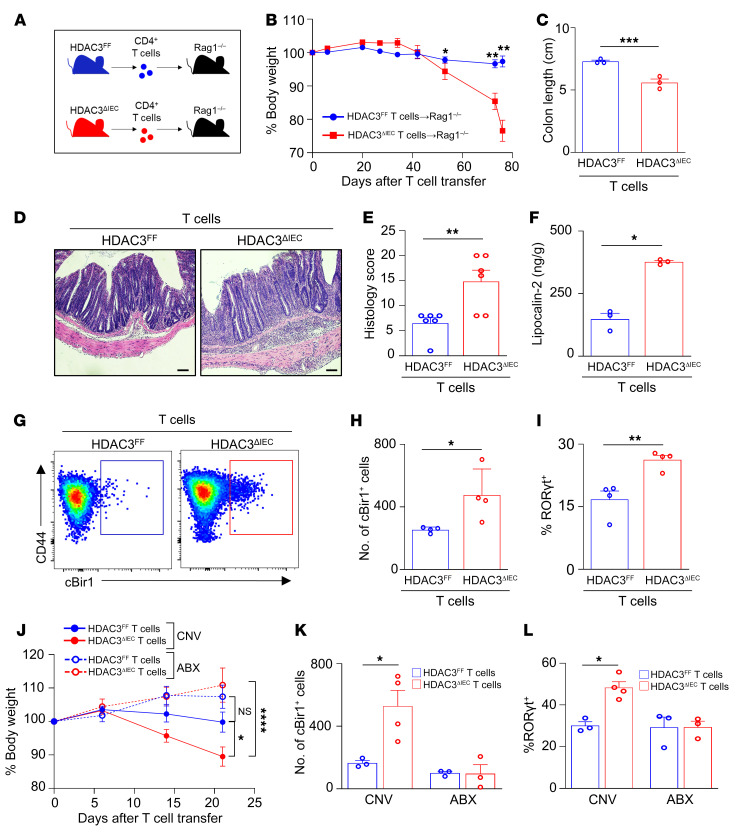
Figure 2. CD4+ T cells from mice lacking epithelial HDAC3 induce severe colitis.
(A) Experimental schematic of T cell colitis model with naive CD4+ T cells isolated from HDAC3FF and HDAC3ΔIEC mice transferred into Rag1–/– hosts. (B–D) Change in body weight (B), colon length (C), and H&E-stained colonic sections (D) of Rag1–/– hosts that received T cells from HDAC3FF or HDAC3ΔIEC mice. Scale bars: 20 μM. (E) Histological scoring of sections in D. (F) Fecal concentration of lipocalin-2. (G and H) Number of cBir1+ tetramer-specific CD4+ T cells in large intestine of Rag1–/– hosts that received T cells from HDAC3FF or HDAC3ΔIEC mice. Gated on live, CD45+, lineage (CD11b–B220–Ly6G–, CD11c–CD8a–), CD4+. (I) Frequency of Th17 (RORγt+) of cBir1+ CD4+ T cells. (J–L) Change in body weight (J), number of cBir1+ tetramer-specific CD4+ T cells (K), and frequency of RORγt+ cBir1+ CD4+ T cells (L) in large intestine of Rag1–/– mice treated with water (CNV) or antibiotics (ABX) that received T cells from HDAC3FF or HDAC3ΔIEC mice. Data are representative of at least 2 independent experiments, 3–4 mice per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, by unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test (B–I) or 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (J–L).