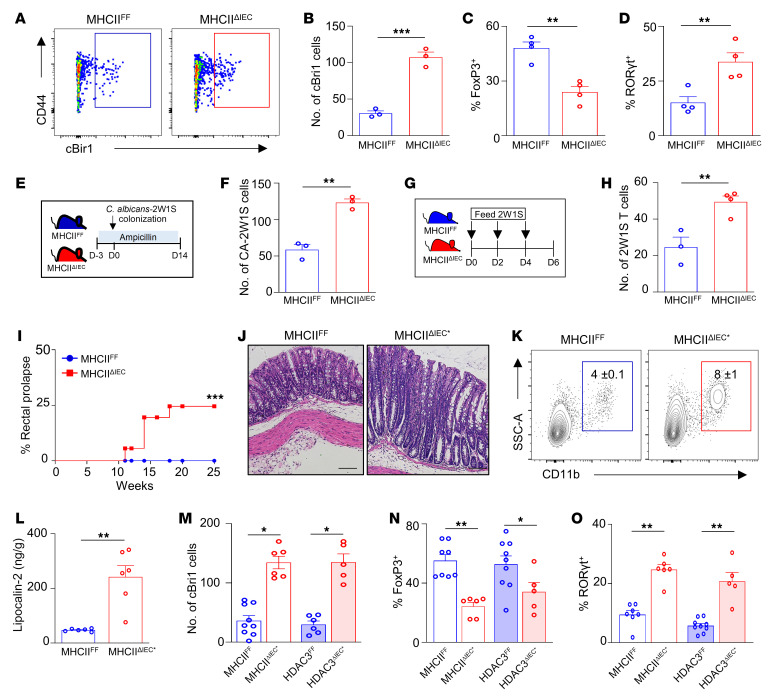
Figure 4. Epithelial MHCII regulates commensal-specific T cells.
(A and B) Number of cBir1+-specific CD4+ T cells in large intestine of MHCIIFF and MHCIIΔIEC mice. (C and D) Frequency of FoxP3+ (C) and RORγt+ (D) cBir1+ CD4+ T cells in large intestine of MHCIIFF and MHCIIΔIEC mice. (E) Diagram of 2W1S–Candida albicans commensal colonization. (F) Number of C. albicans–2W1S+–specific CD4+ cells in large intestine of MHCIIFF and MHCIIΔIEC mice. (G) Diagram of 2W1S peptide feeding model. (H) Number of 2W1S+-specific CD4+ cells in large intestine of MHCIIFF and MHCIIΔIEC mice. (I) Frequency of rectal prolapse in MHCIIFF and MHCIIΔIEC mice. (J) H&E-stained colonic sections of MHCIIFF and prolapsed MHCIIΔIEC mice (MHCIIΔIEC*). Scale bars: 20 μM. (K and L) Frequency of myeloid cell infiltrate (K) and lipocalin-2 levels (L) in stool of MHCIIFF and MHCIIΔIEC*. (M–O) Number of cBir1+-specific CD4+ T cells (M) and frequency of FoxP3+ (N) and RORγt+ (O) cBir1-specific T cells in large intestine of control and prolapsed MHCIIΔIEC and HDAC3ΔIEC mice. Tetramer cells are gated on live, CD45+, lineage (CD11b–B220–Ly6G–, CD11c–CD8a–), CD4+. Data are representative of at least 2 independent experiments (A–H) or are pooled from at least 2 independent experiments (I–O), 3–6 mice per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, by unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test (B–H and L–O) or Mantel-Cox test (I).