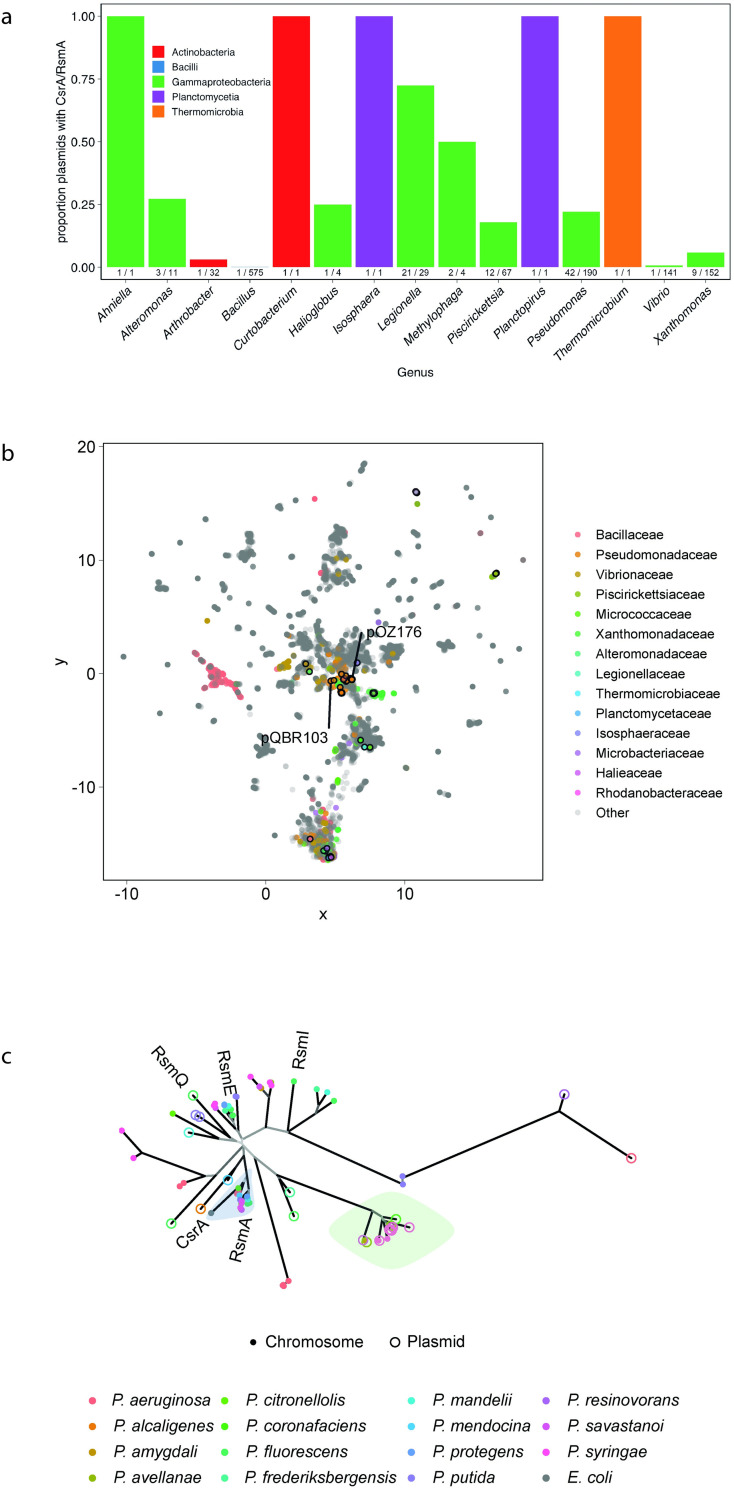
Fig 1. RsmQ is found on a wide range of conjugative plasmids.
(a) Taxonomic distribution of plasmid borne csrA/rsmA homologues identified in COMPASS. (b) COMPASS plasmid diversity represented by NMDS of MASH sequence distances. Families with ≥1 plasmid with a csrA/rsmA homologue are coloured according to the legend. Plasmids encoding csrA/rsmA homologues are outlined in black. Selected plasmids from various taxa are annotated. (c) Unrooted phylogenetic tree of Pseudomonas csrA/rsmA homologues from COMPASS, with corresponding chromosomal homologues (where available) and genes from selected reference strains. Branches leading to nodes with >80% bootstrap support are coloured black, with decreasing support indicated with increasingly pale grey. P. fluorescens SBW25 csrA/rsmA homologues are labelled, as is pQBR103 rsmQ, and E. coli csrA. The blue highlight indicates a well-supported (bootstrap support 0.84) group of rsmA-like homologues. The green highlight indicates the group of related plasmid and chromosomal genes from plant pathogen Pseudomonas discussed in the text. All data and analyses are available on github (PLASMAN_RsmQ) with data taken from the COMPASS database. NMDS, non-metric multidimensional scaling.