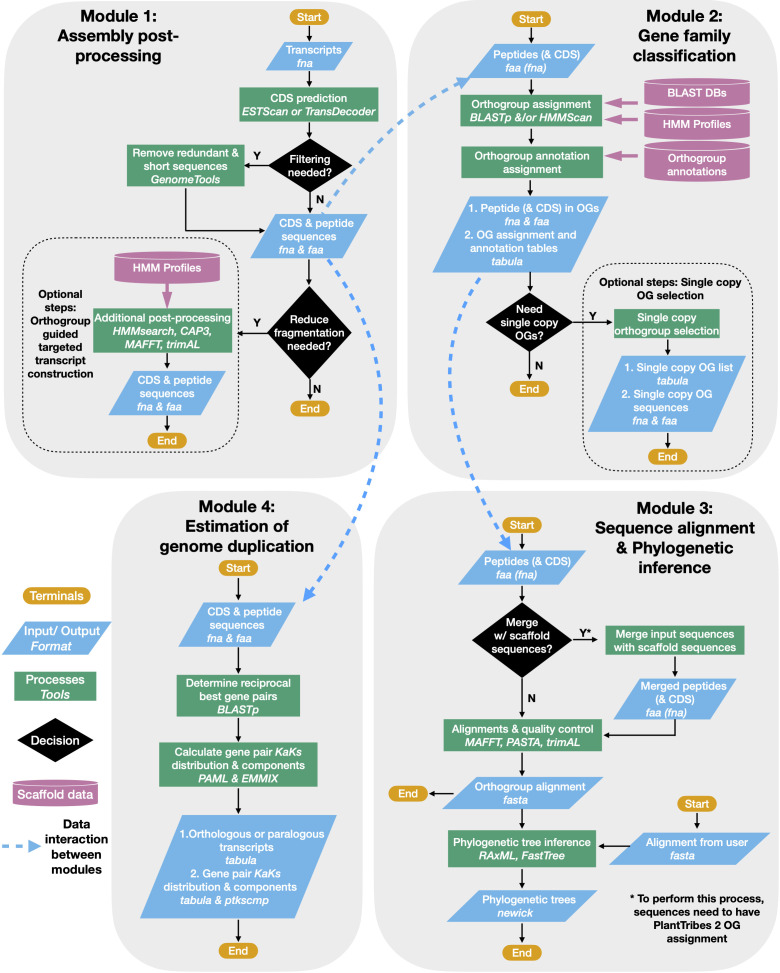
Figure 1.
PlantTribes2 analysis workflow. A schematic diagram illustrating the PlantTribes2 modular analysis workflow. (1) A user provides transcripts for post-processing, resulting in a non-redundant set of predicted coding sequences and their corresponding translations (Module 1). (2) The post-processed transcripts (or user provided sequences) are searched against a gene family scaffold blast and/or hmm database(s), and transcripts are assigned into their putative orthogroups with corresponding metadata (Module 2). (3) Classified transcripts are integrated with their corresponding scaffold gene models to estimate orthogroup multiple sequence alignments and corresponding phylogenetic trees (Module 3). Similarly, sequence alignments and phylogeny can be constructed from user provided data. (4) Synonymous substitution rate (Ks) and nonsynonymous substitution rate (Ka) of paralogs from either the post-processed assembly or inferred from the phylogenetic trees are estimated. The Ks results are used to detect large-scale duplication events and many other evolutionary hypotheses (Module 4).