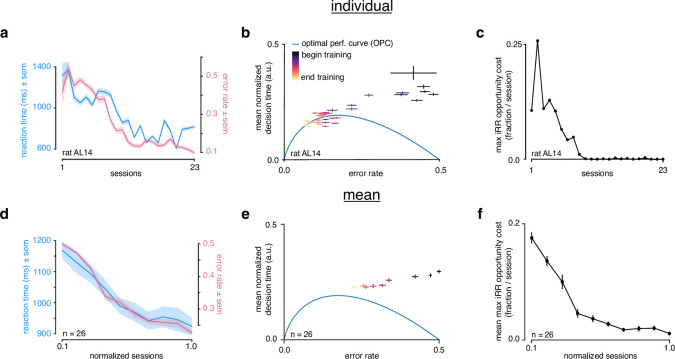
Figure 2. Rats do not greedily maximize instantaneous reward rate during learning.
(a) Reaction time (blue) and error rate (pink) for an example subject (rat AL14) across 23 sessions. (b) Learning trajectory of individual subject (rat AL14) in speed-accuracy space. Color map indicates training time. Optimal performance curve (OPC) in blue. (c) Maximum opportunity cost (see Methods) for individual subject (rat AL14). (d) Mean reaction time (blue) and error rate (pink) for rats during learning. Sessions across subjects were transformed into normalized sessions, averaged and binned to show learning across 10 bins. Normalized training time allows averaging across subjects with different learning rates (see Methods). (e) Learning trajectory of rats in speed-accuracy space. Color map and OPC as in a. (f) Maximum opportunity cost of rats in b throughout learning. Errors reflect within-subject session SEMs for a and b and across-subject session SEMs for d, e, and f.