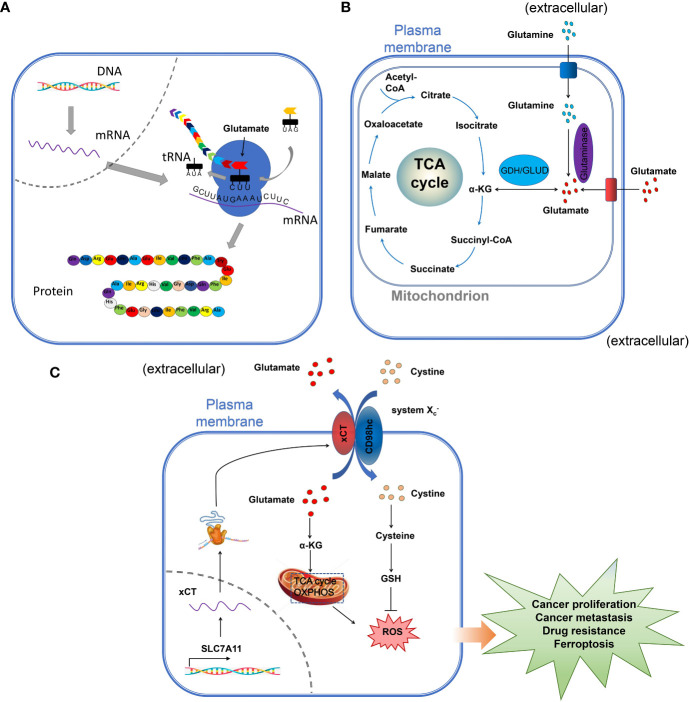
Figure 1.
The role of glutamate in cells. (A) the role of glutamate in protein synthesis. The amino-acid glutamate is the substrate for protein synthesis, important for the maintenance and promotion of cell function. (B) the role of glutamate in the TCA. Extracellular glutamate is one of the most important sources of carbon in The TCA cycle. In the mitochondria, glutamate is deaminated to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) by glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), which is incorporated in the TCA cycle for energy production. (C) glutamate and the maintenance of cell homeostasis and regulation of cell proliferation. The amino-acid exchangers also known as cystine-glutamate transporter (xCT/SLC7A11), play a very important role in maintaining redox homeostasis by exchanging extracellular cystine in exchange for intracellular glutamate to maintain intracellular redox and the energy production for the regulation of cell proliferation.