Figure 3.
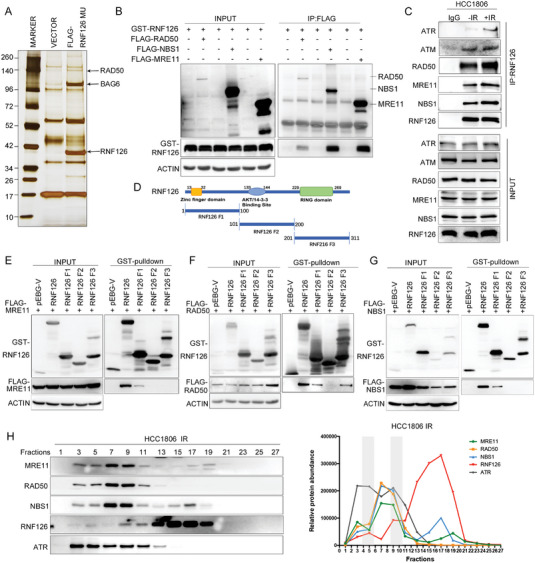
RNF126 is physically associated with MRN and ATR. A) Immunopurification and mass spectrometric analysis of RNF126‐containing protein complexes. Cellular extracts from HCC1806 cells stably expressing FLAG‐RNF126 C292/232A were immunopurified with anti‐FLAG affinity beads and eluted with FLAG peptide. The eluates were resolved on SDS/PAGE and silver stained, followed by mass spectrometric analysis. B) GST‐RNF126 was co‐immunoprecipitated by each FLAG‐tagged MRN protein. GST fused RNF126 and FLAG‐RAD50, FLAG‐NBS1, or FLAG‐MRE11 were expressed in HEK293T cells. GST‐pulldown was used to detect the association between RNF126 and the MRN complex. C) Endogenous RNF126 interacted with MRN, ATM, and ATR. HCC1806 cells were treated with or without IR (10 Gy), and 1 h after IR, cellular extracts were harvested for coimmunoprecipitation followed by Western blotting analysis. D) Schematic of RNF126 fragments. E–G) N‐terminus of RNF126 interacted with MRE11 and NBS1. Map of E) MRE11, F) RAD50, or G) NBS1 interaction domains of RNF126. Different GST‐fused RNF126 fragments and FLAG‐MRE11, FLAG‐RAD50, or FLAG‐NBS1 were expressed in HEK293T cells. Then GST‐pulldown was used to detect the association between RNF126 fragments and the MRN complex. H) Native RNF126 was co‐eluted with MRN complex and ATR. FPLC analysis of the native protein complex. Cellular extracts from HCC1806 cells after 1 h post‐IR (10 Gy) were fractionated on Superose 6 size‐exclusion columns with a high‐salt buffer. Western blotting analysis of the chromatographic fractions with antibodies against the indicated proteins. Equal volumes from each fraction were analyzed and the boxed area indicates fractions in which endogenous RNF126 was co‐eluted with the MRN complex. The amounts of the indicated proteins were quantified using ImageJ.
