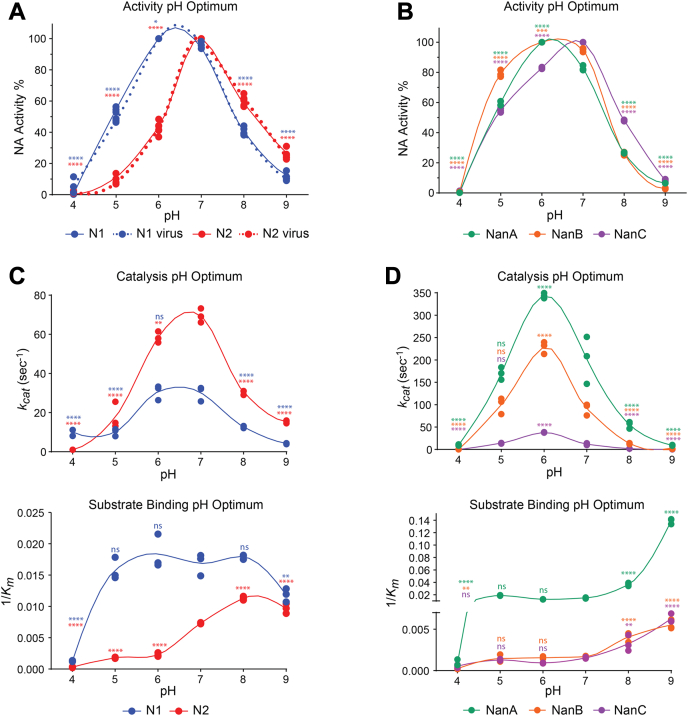
Figure 3.
Variation in neuraminidase activities by pH and the contributing properties.A, recombinant N1 and N2 activities were determined using buffers at the indicated pH values using MUNANA. The highest activity for each enzyme was set to 100% and used for normalization. Viruses containing identical full-length N1 and N2 were included as controls. B, recombinant NanA, NanB, and NanC activities were determined at the indicated pH values using MUNANA. The highest activity for each enzyme was set to 100% and used for normalization. C, graphs displaying the (upper panel) catalytic rate (kcat) and (lower panel) reciprocal Michaelis constant (Km) for N1 and N2 that were determined at each pH using MUNANA. D, NanA, NanB, and NanC (upper panel) kcats and (lower panel) reciprocal Kms were determined at each pH using MUNANA. p values were generated by a one-way ANOVA Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test with a 95% CI with pH 7 as the comparison condition to characterize an increase or decrease in activity due to changes away from neutral pH. ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗p ≤ 0.05, ns p > 0.05. MUNANA, 4-methylumbelliferyl-α-D-N-acetylneuraminide.