Figure 2.
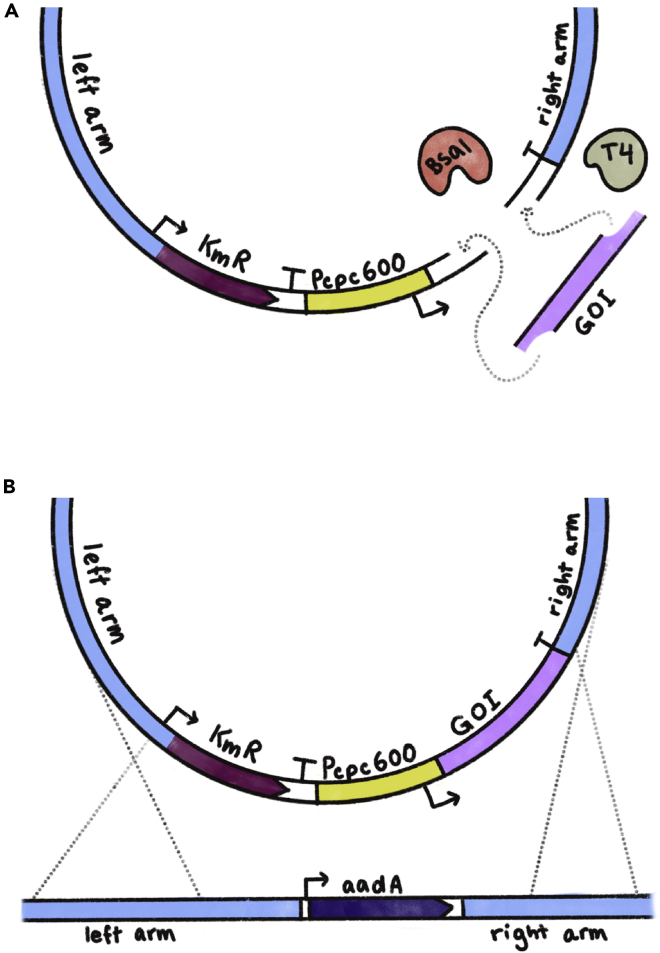
Schematic of shuttle vector cloning using Golden Gate and its subsequent homologous recombination into the A. platensis genome
(A) A simple representation of the Golden Gate cloning process. The BsaI restriction enzyme cleaves both the backbone plasmid and the gene of interest (“GOI”) PCR-amplified fragment. The compatible sticky ends are then ligated together by the T4 DNA ligase for the generation of the final shuttle vector.
(B) The shuttle vector carrying the GOI is introduced into the A. platensis cell, where it is inserted into the targeted locus via homologous recombination. In this diagram, the insertion occurs at the modified KmR site carrying the aadA streptomycin resistance gene.