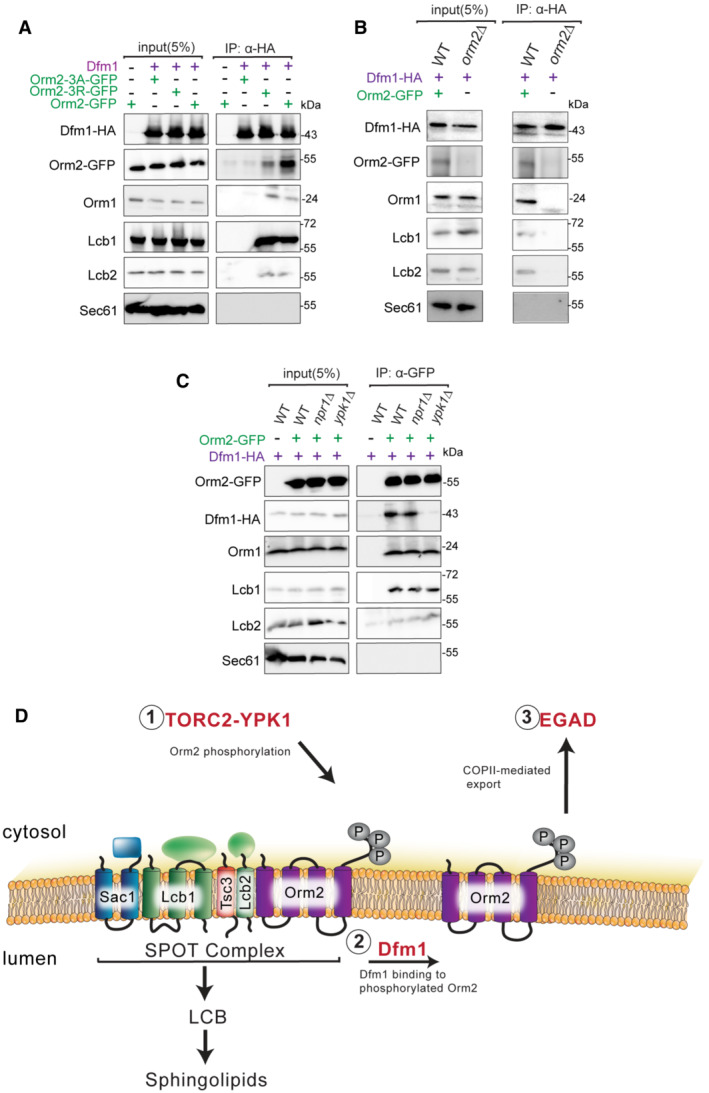
Dfm1‐HA binding to Orm2‐GFP, Orm2‐3A‐GFP, Orm2‐3D‐GFP, Orm1, Lcb1, and Lcb2 was analyzed by co‐IP. As a negative control, cells not expressing Dfm1‐HA were used. Also, Sec61 was also included to test for non‐specific binding (3 biological replicates; n = 3).
Same as (A), except co‐IP was performed on WT and orm2∆ cells and Dfm1‐HA binding to Orm1, Lcb1, and Lcb2 was analyzed (3 biological replicates; n = 3).
Same as (A), except Orm2‐GFP binding to Dfm1‐HA, Orm1, Lcb1, and Lcb2 was analyzed by co‐IP (3 biological replicates; n = 3).
Schematic of Dfm1's role in Orm2 degradation. (i) Orm2 is inactivated via phosphorylation by the TORC2‐YPK1 signaling axis. (ii) Dfm1 binds phosphorylated Orm2. (iii) Phosphorylated Orm2 is delivered to COPII vesicles. (iv) Phosphorylated Orm2 is routed to the Golgi and degraded via EGAD.