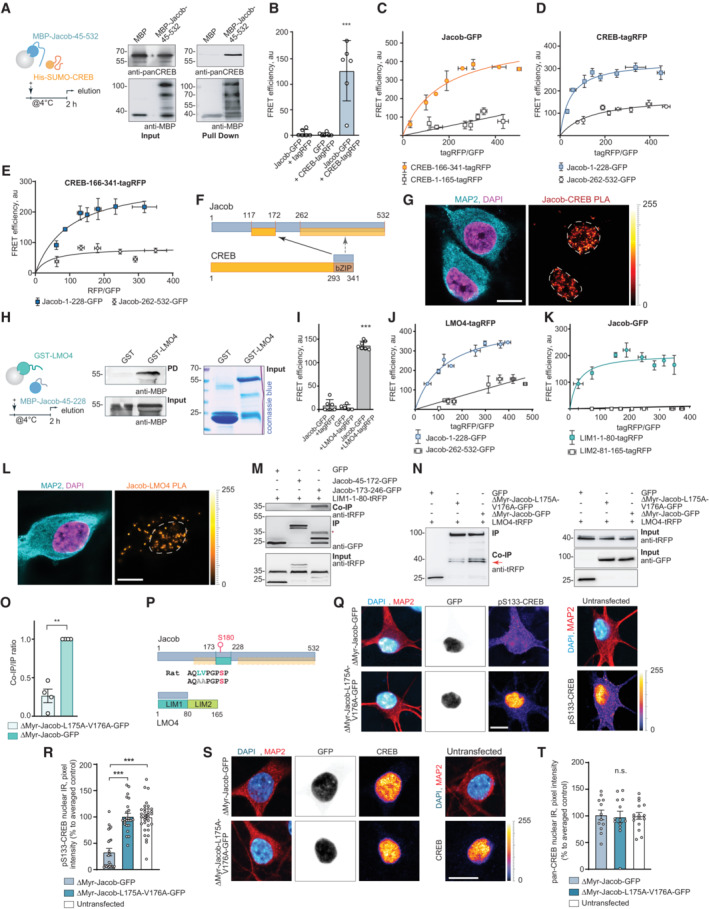
Figure 2. Jacob directly associates with cAMP‐responsive element‐binding protein (CREB) and LMO4.
-
APull‐down assays confirm a direct interaction of MBP‐Jacob‐45‐532 and His‐SUMO‐CREB.
-
BFluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) measurements show an association between CREB‐tagRFP and Jacob‐GFP. N = 5 independent experiments measured in triplicates.
-
C–E(C) The C‐terminus (CREB‐166‐341‐tagRFP) but not the N‐terminus (CREB‐1‐165‐tagRFP) of CREB closely associates with Jacob‐GFP in FRET saturation experiments. (D) Both the N‐ (Jacob‐1‐228‐GFP) and the C‐terminus (Jacob‐262‐532‐GFP) of Jacob are in close proximity to CREB‐tagRFP; however, the Jacob‐1‐228‐GFP association with CREB is significantly stronger. (E) The C‐terminus of CREB (CREB‐166‐341‐tagRFP) associates prominently with the N‐terminus (Jacob‐1‐228‐GFP) and less strong with the C‐terminus (Jacob‐262‐532‐GFP) of Jacob. (C–E) FRET efficiency is presented in arbitrary units from 5 to 6 independent experiments.
-
FBinding interfaces between CREB and Jacob.
-
GA proximity ligation assay revealed an interaction between Jacob and CREB in primary neurons. Dashed ROIs indicate neuronal nuclei. Scale bar: 10 μm.
-
HGST‐LMO4 but not GST alone directly binds to MBP‐Jacob‐45‐228. From left to right: A scheme depicting experimental procedure, image of membrane probed with anti‐MBP antibody, and the Coomassie blue‐stained gel showing the purity of proteins used as an pull‐down input.
-
IFRET experiments revealed that Jacob‐GFP interacts with LMO4‐tagRFP. N = 5–7 independent experiments measured in triplicates.
-
J, KFRET saturation experiments indicate the association of Jacob‐1‐228‐GFP with LIM‐1‐80‐tagRFP. FRET efficiency is presented in arbitrary units as a mean of 6 independent experiments measured in triplicates.
-
LA proximity ligation assay revealed an interaction between Jacob and LMO4 in primary neurons. Scale bar: 10 μm.
-
MCo‐immunoprecipitation experiments to map the binding region of Jacob to the LIM1 domain of LMO4 revealed the association with Jacob‐179‐246‐GFP, but not with Jacob‐45‐172‐GFP (CREB‐binding region).
-
N, OHeterologous co‐immunoprecipitation experiments between LMO4‐tagRFP and nuclear ΔMyr‐Jacob‐GFP, ΔMyr‐Jacob‐L175A‐V176A‐GFP or GFP point to a decreased association of ΔMyr‐Jacob‐L175A‐V176A‐GFP with LMO4 as compared to ΔMyr‐Jacob‐GFP. N = 4 independent experiments.
-
PBinding interfaces between Jacob and LMO4.
-
Q–TA Jacob‐LMO4‐binding mutant expressed in the nucleus does not induce CREB shutoff. (Q, S) Representative confocal images of hippocampal neurons transfected with ΔMyr‐Jacob‐GFP (Jacob targeted to the nucleus) or ΔMyr‐Jacob‐L175A‐V176A‐GFP. Scale bar: 10 μm. Lookup table indicates the pixel intensities from 0 to 255. (R, T) The mean of nuclear (R) pCREB or (T) CREB immunoreactivity in Jacob‐expressing neurons was normalized to non‐transfected controls. N = 23–33 neuronal nuclei from two independent cell cultures.
Data information: **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by (O) one‐sample t‐test or one‐way ANOVA followed by (B, I) Bonferroni's or (R, T) Tukey's multiple comparisons test. All data are represented as mean ± SEM.
Source data are available online for this figure.
