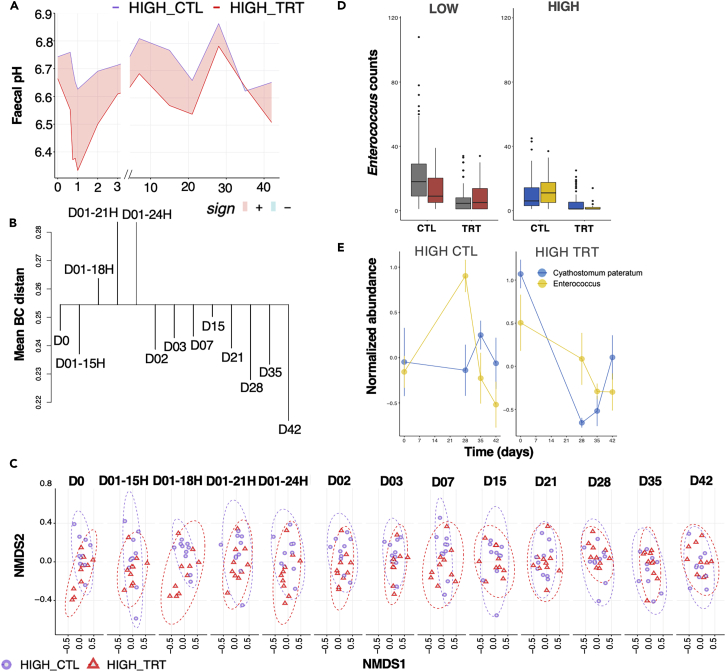
Figure 5.
Parasite removal has a drastic and acute effect on the gut environment and microbiota composition, but a limited response in the host blood transcriptome
(A) Evolution of fecal pH across time in high shedders. To display differences between group series, the ribbon was filled with red color when the max in HIGH-CTL was higher than the min in HIGH-TRT, and in cyan color when the maximum in HIGH-TRT was higher than the min in HIGH-CTL.
(B) Dendrogram plot based on the within-time and between time dissimilarities in the HIGH-TRT group. The leaf segment is reversed if some time points are more heterogeneous than the combined time class. The horizontal line is drawn at the level of mean between-time dissimilarity, and vertical lines connect within-time dissimilarities to this line.
(C) NMDS ordination analysis (Bray-Curtis distance) of the ASV composition in HIGH_CTL (violet), and HIGH_TRT (red) samples across the time points.
(D) Enterococcus count distribution in the untreated (CTL) and treated (TRT) low- and high-shedders. Boxplots are colored according to whether counts were measured before (gray or blue) or after (red or yellow) significant parasite reappearance period (28 days after pyrantel treatment). Boxes show median and interquartile range, and whiskers indicate the 5th to 95th percentile.
(E) Trajectory of Enterococcus and Cyathostomum pateratum in the untreated and treated high shedders. Dots represent the mean and standard deviation of each time point.