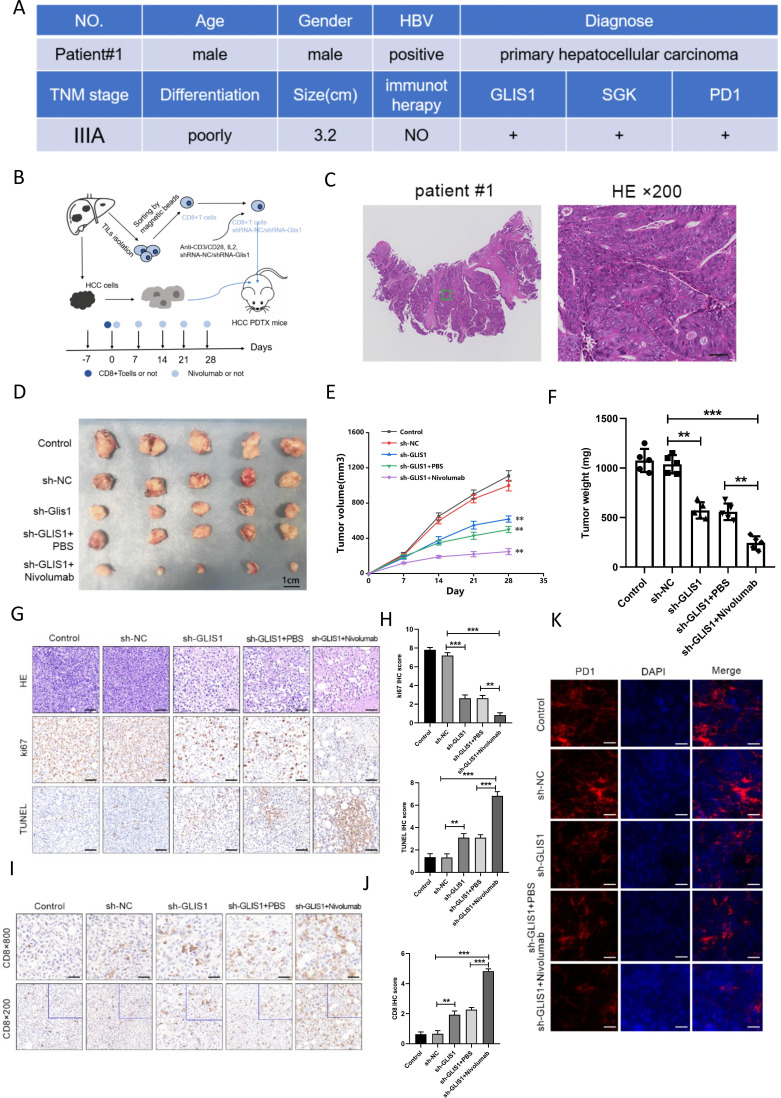
Figure 5.
GLIS1 knockdown alleviated CD8+ T cell exhaustion and improved the response to αPD1 therapy in PDX model of HCC. (A) Basic clinical information of the HCC patient used for PDX model. (B) Schematic diagram of the mouse experiment. CD8+ TIL cells from patients with HCC were pretreated with a control interfering lentivirus (shRNA-NC) or an interfering lentivirus targeting the GLIS1 gene (sh-GLIS1) and the cells were subsequently adoptively transferred into NOD/SCID mice-harboring HCC PDX with or without αPD1 therapy. (C) The tumors were confirmed by HE staining in HCC patient used for PDX model. (D) Picture display of the respective group (Control, sh-NC, sh-GLIS1, sh-GLIS1+PBS, sh-GLIS1+αPD1) of subcutaneous tumors. (E) The volume and (F) weight statistics of subcutaneous tumors in the respective group (Control, sh-NC, sh-GLIS1, sh-GLIS1+PBS, sh-GLIS1+αPD1). (G, H) The tumors were confirmed by HE staining. Immunohistochemical results of Ki67 and TUNEL expression in the respective group. (I, J) Immunohistochemical results of CD8 expression in the respective group. (K) Immunofluorescence results of PD1 expression in the respective group. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; PDX, patient-derived xenograft.