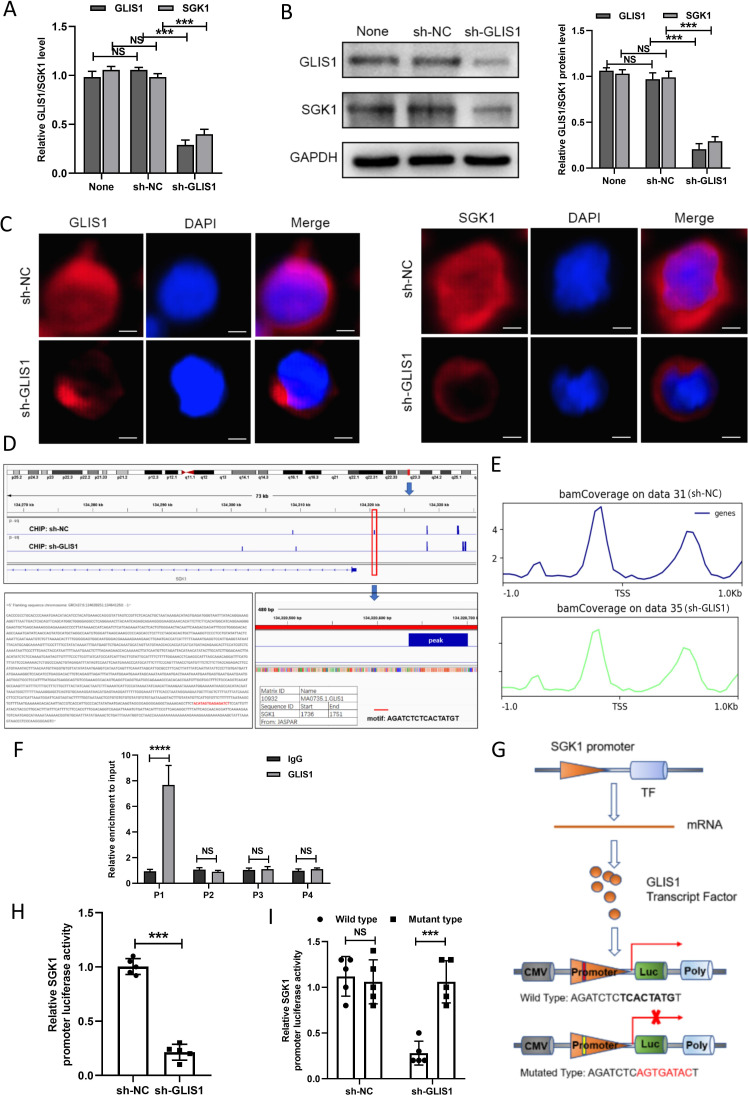
Figure 7.
GLIS1 promoted the exhaustion of CD8+ T cells by targeting SGK1 in HCC. (A) qRT-PCR revealed the expressions of GLIS1 and SGK1 under GLIS1 knockdown in CD8+ T cells. (B) Western blotting revealed the expressions of GLIS1 and SGK1 under GLIS1 knockdown in CD8+T cells. (C) Immunofluorescence results of GLIS1 and SGK1 expression under GLIS1 knockdown in CD8+ T cells. (D) Our CHIP sequencing results of the peak in sh-NC group and sh-GLIS1 group. (E) Possible binding sites of GLIS1 and SGK1 in transcription start site (TSS). (F) CHIP assay confirmed that GLIS1 can be directly correlated with the SGK1 promoters within P1, while it has no obvious significance in other sites (P2, P3, P4). (G) Schematic diagram of the dual luciferase assay. (H) SGK1 promoter-driven reporter activity was measured under GLIS1 downexpression. (I) The luciferase reporter gene experiment revealed the result of the mutated and wild type sequence affecting the promoter-driven reporter activity of SGK1 under GLIS1 down-expression. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. NS indicates no significant difference. CHIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; qRT-PCR, quantificational real-time PCR.