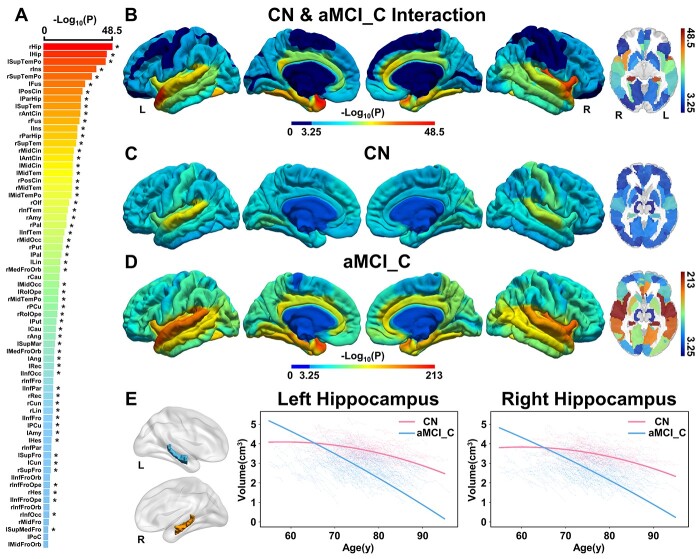
Fig. 2.
Cerebral longitudinal atrophic trajectories following aging in CN and aMCI_C groups. (A) The ordered -log10(P) values of cerebral regions with significantly accelerated cerebral atrophy following age in aMCI_C relative to CN. A linear mixed-effects model was used to estimate the quadratic cerebral atrophic differences between the groups (P < 0.05/90, Bonferroni correction). Asterisk (*) indicates cerebral regions that the AAL3 atlas can validate. (B) The cortical maps of the group differences in quadratic cerebral atrophy as a function of aging. Color bar represents the -log10(P) values. Dark blue represents non-significant. (C) and (D) represents -log10(P) values of the quadratic cerebral atrophy as a function of aging in CN and aMCI_C, respectively. (E) Age-related atrophy changes in the hippocampus. Solid red (CN) and blue (aMCI_C) lines represent the fitted GMV change as a function of aging. The full names of the brain regions are shown in Supplementary Table 4. Abbreviations: aMCI_C = amnestic mild cognitive impairment converters; CN = cognitively normal; GMV = gray matter volume; L = left; R = right; y = year.