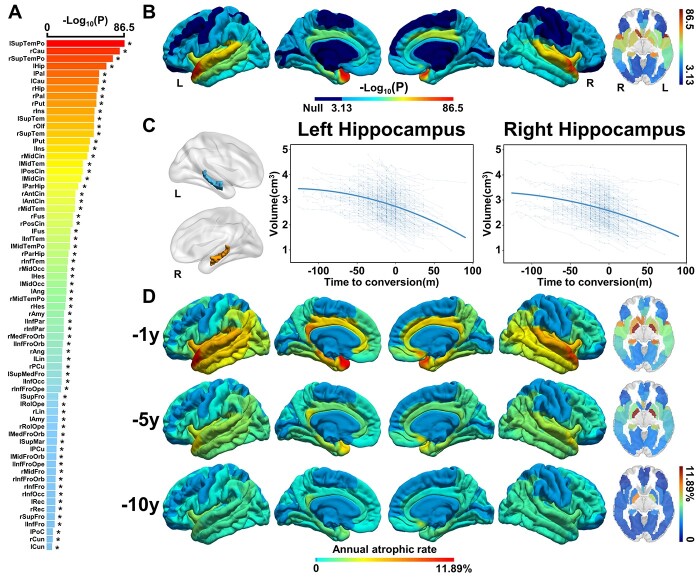
Fig. 4.
Cerebral longitudinal atrophic trajectories from aMCI to AD. (A) The ordered -log10(P) values of cerebral regions with significantly accelerated cerebral atrophy from aMCI to AD. A linear mixed-effects model was used to estimate the quadratic cerebral atrophic trajectories as a function of time to AD conversion (P < 0.05/68, Bonferroni correction). Asterisk (*) indicates cerebral regions that the AAL3 atlas can validate. (B) The quadratic cerebral atrophic maps as a function of time to AD conversion. The color bar represents the -log10(P) values. Dark blue represents non-significant. (C) The atrophic trajectories of the hippocampus during the conversion. Solid blue lines represent the fitted hippocampal volume as a function of time to AD conversion. (D) The maps of average annual atrophic rate within 1 year, 5, and 10 years prior to AD conversion. The full names of the brain regions are shown in Supplementary Table 6. Abbreviations: L = left; m = month; R = right.