Figure 4. Mean Values for Overall Average RNFL Thickness (360° Around the Optic Disc) and for RNFL Thickness in Temporal, Superior, Nasal, and Inferior Quadrants for Patients With Multiple Sclerosis (MS; n = 90 [180 Eyes]) and Disease-Free Controls (n = 36 [72 Eyes]).
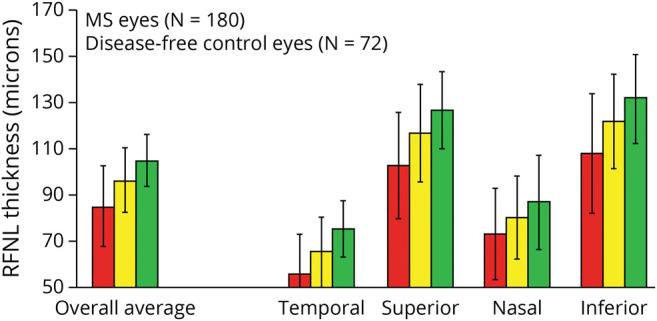
*Average overall RNFL thickness values were significantly lower for patients with MS vs controls (p < 0.001, generalized estimating equation [GEE] models accounting for age and adjusting for within-patient intereye correlations). †Mean RNFL thickness values varied significantly across retinal quadrants (p < 0.0001), with mean thickness greater in the superior and inferior quadrants. The mean thickness was greater for controls than for patients with MS in all quadrants, and the difference between patient groups was of the same magnitude in each quadrant (p = 0.34 for interaction terms, GEE models). GEE = generalized estimating equation; MS = multiple sclerosis; RNFL = generalized estimating equation.
