Fig. 1. Comparison between Bayesian and frequentist approaches.
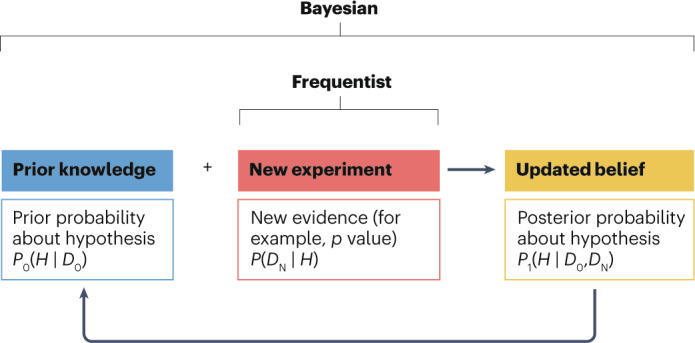
The frequentist approach evaluates evidence from a single new experiment, most often using a p value as a measure for deciding whether a hypothesis is true or false. The Bayesian approach formally and statistically quantifies prior knowledge (D0) about a hypothesis (H) in the form of a prior probability (P0), which is then combined with the evidence from a new experiment (DN) to compute a posterior probability (P1) about the veracity of that hypothesis. The posterior probability can be recycled as input to form the prior for a subsequent experiment, thereby creating a virtuous cycle of synthesizing scientific knowledge about a hypothesis.
