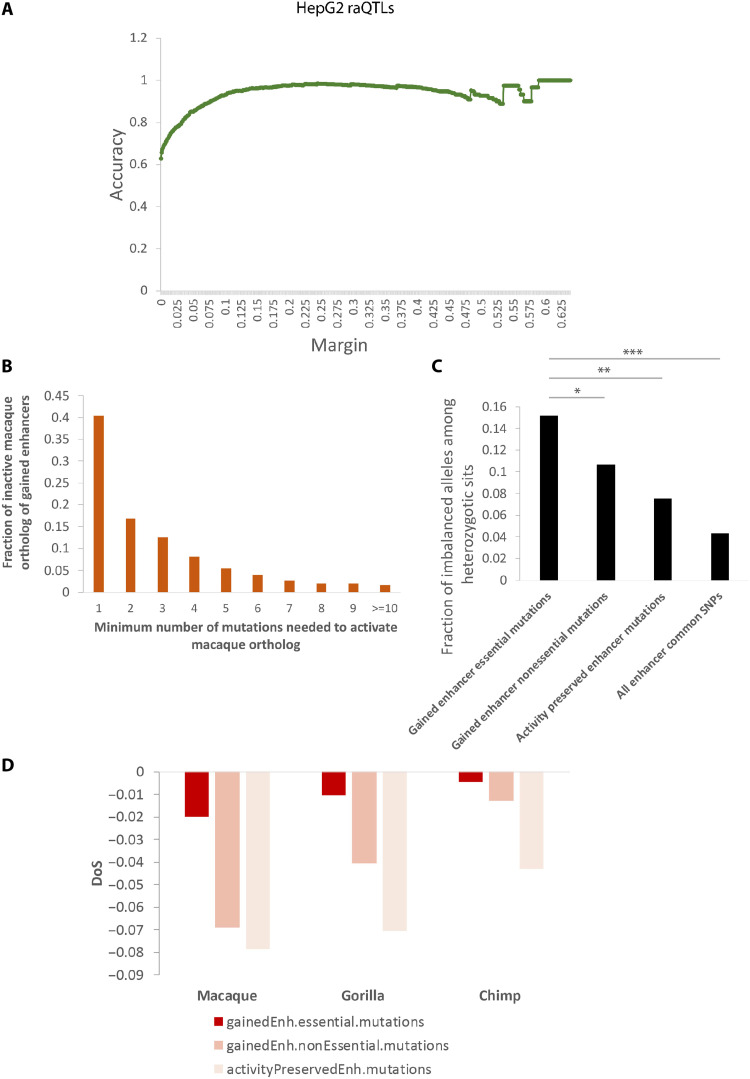
Fig. 4. Essential mutations show larger impact on enhancer activity.
(A) Deep learning enhancer classifiers in HepG2 accurately predicted allele-specific effects on enhancer activity (the allele with stronger enhancer activities). The predictions were evaluated with regulatory activity QTLs (raQTLs) identified in HepG2 cell lines (52). Margin shown on the x axis is the threshold of predicted probability differences between the two alleles for classifying high-confidence predictions. Performance is measured by accuracy (y axis) of predicting the allele with higher enhancer activities based on DLM score difference above certain threshold (x axis). (B) Fraction of de novo gained enhancers that could be activated by specific number of mutations. (C) Fraction of mutation/SNP sites that are in allelic imbalance. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 1 × 10−3, Fisher’s exact test. (D) DoS score of the mutated sites, using macaque, gorilla, and chimp as comparison species.