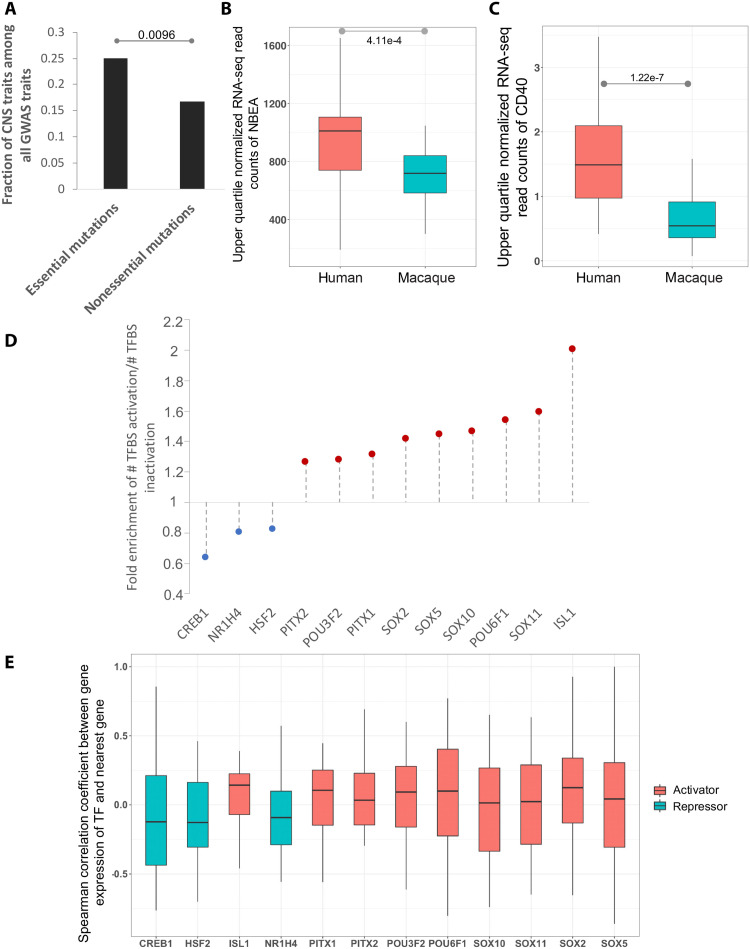
Fig. 5. Essential mutations are associated with cognition-related traits and tend to create binding sites of activators.
(A) Fraction of GWAS traits at the mutation sites that are CNS-related. (B) Comparison of trimmed mean of M values (TMM)-normalized expression of NBEA between embryonic human and rhesus macaque individuals. P values are based on the Wilcoxon test. (C) Comparison of TMM-normalized expression of CD40 between embryonic human and rhesus macaque individuals. P values are based on the Wilcoxon test. (D) Enrichment of ratio of binding site gain to loss caused by essential mutations overlapping enriched TFBSs as compared to those caused by common SNPs. (E) Spearman correlation coefficient of expression between the cognate TF of essential mutation and its nearest gene.