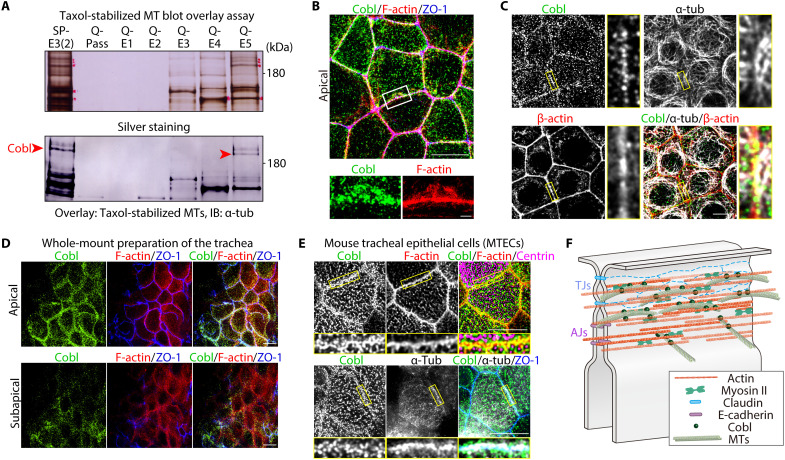
Fig. 1. Cobl was identified as an AJC-enriched, MT-associated protein.
(A) Membrane overlay assays of taxol-stabilized MTs using the AJC-enriched BC fraction (see also fig. S1). Immunoblotted bands marked by red arrowheads correspond to Cobl. (B) Representative superresolution micrographs of immunostained Eph4 epithelial cells in the apical plane (see also movie S1). Scale bar, 10 μm (low magnification) and 1 μm (high magnification). (C) In Eph4 cells, Cobl was closely associated with both actin and MTs at cell-cell junctions. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) In the in vivo trachea, similarly to cultured Eph4 epithelial cells, Cobl localized to cell-cell junctions at the apical and subapical planes. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Cobl was also closely associated with both F-actin and MTs at the AJC in mouse tracheal epithelial cells (MTECs). Scale bar, 5 μm. (F) Schematic drawing of Cobl localization at the AJC in association with actomyosin-based CR and MTs.