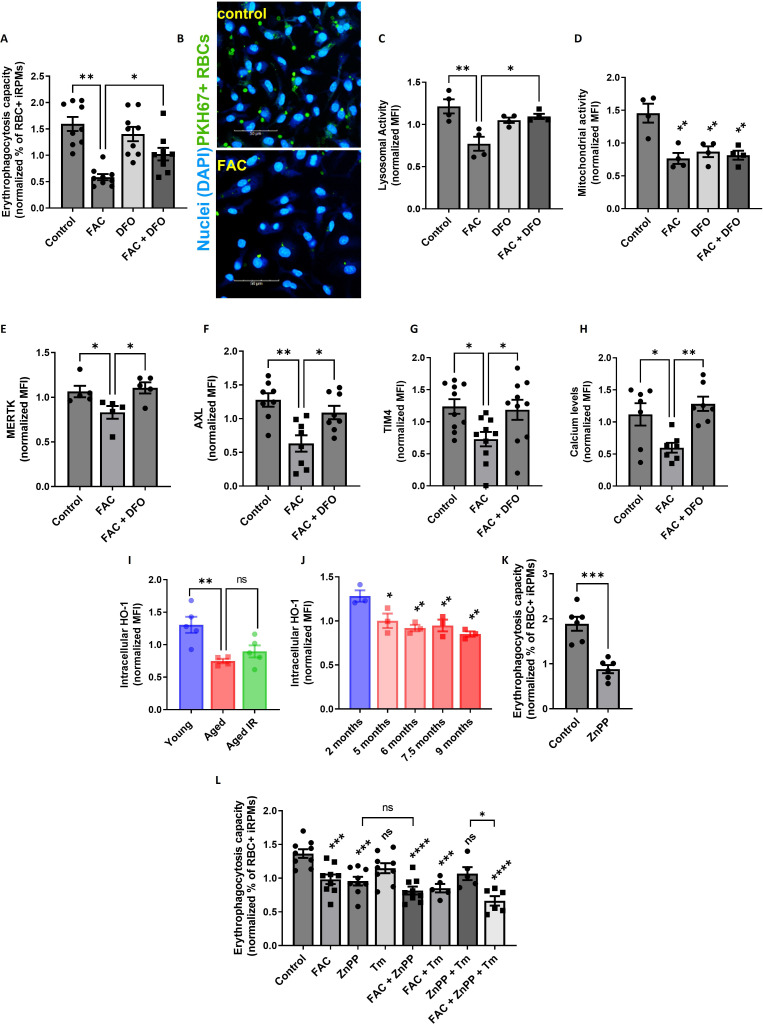
Figure 6. Iron loading undermines the phagocytic activity of iRPMs in concert with impaired heme metabolism and ER stress.
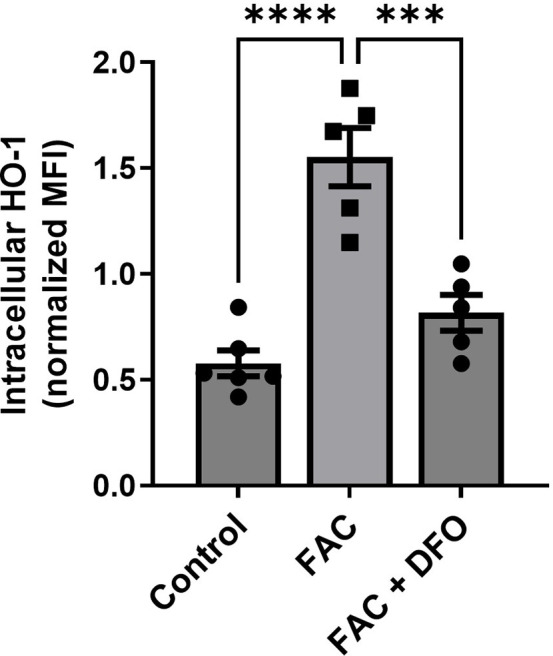
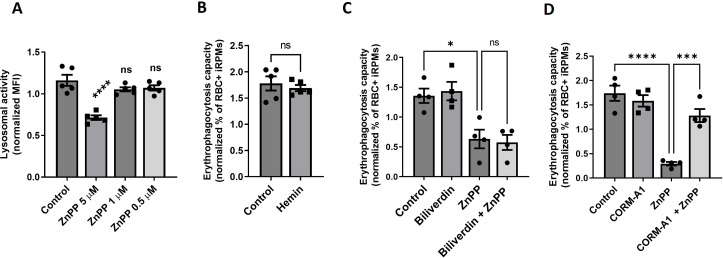
(A) Normalized erythrophagocytosis capacity of PKH67-labeled temperature-stressed RBCs by cultured iRPMs. Cells were treated with FAC (50 µM, 24 hr) and DFO (100 µM, 18 hr) as indicated. (B) Representative confocal microscopy images of erythrophagocytosis in FAC-treated iRPMs compared with control cells. (C) Lysosomal and (D) mitochondrial activity of cultured iRPMs were determined using Lysosomal Intracellular Activity Assay Kit and TMRE probe, respectively, with flow cytometry. Cells were treated with FAC (50 µM, 24 hr) and DFO (100 µM, 18 hr) as indicated. (E) Cell membrane expression levels of MERTK, (F) AXL and (G) TIM4 of cultured iRPMs were determined by using fluorescently labeled antibodies and flow cytometry. Cells were treated with FAC (50 µM, 24 hr) and DFO (100 µM, 18 hr) as indicated. (H) Cytosolic calcium levels of cultured iRPMs were determined using Cal-520 fluorescent probe with flow cytometry. Cells were treated with FAC (50 µM, 24 hr) and DFO (100 µM, 18 hr) as indicated. (I) Intracellular HO-1 protein levels in RPMs isolated from young, aged, and aged IR mice were measured by flow cytometry. (J) Intracellular HO-1 protein levels in RPMs isolated from mice at the indicated age were measured by flow cytometry. (K) Normalized erythrophagocytosis capacity of PKH67-labeled temperature-stressed RBCs by cultured iRPMs. Cells were treated with ZnPP (0.5 µM, 24 hr). (L) Normalized erythrophagocytosis capacity of PKH67-labeled temperature-stressed RBCs by cultured iRPMs. Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of ZnPP (0.5 µM) and FAC (10 µM) and with ER stress inducer Tunicamycin (Tm; 2.5 µM) for 24 hr. Each dot represents one mouse or independent cell-based experiment. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance among the three or more groups was determined by One-Way ANOVA test with Dunnett’s or Tukey’s Multiple Comparison test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001.
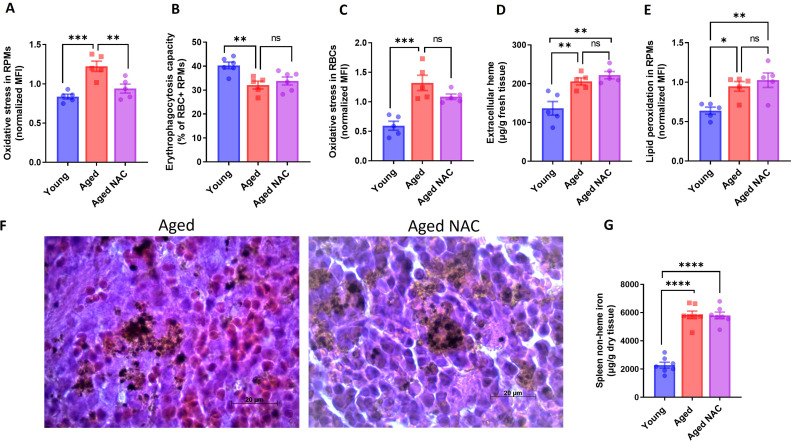
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Iron loading, but not oxidative stress leads to RPM decline during aging.
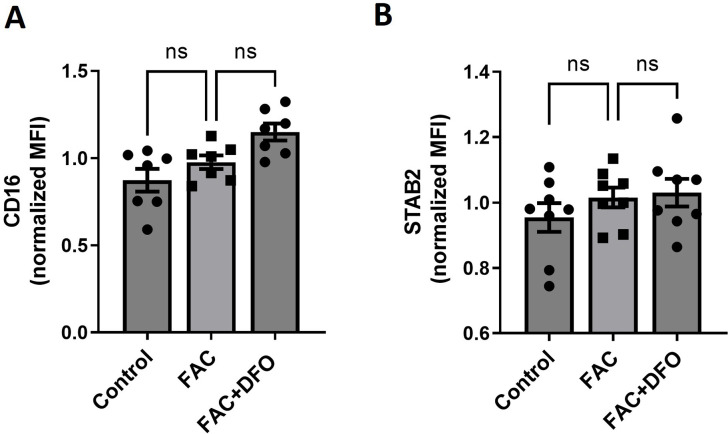
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. The Fc receptor CD16 and the apoptotic cell receptor STAB2 are not regulated by iron-loading.
Figure 6—figure supplement 3. Validation of the antibody against HO-1 in flow cytometry.