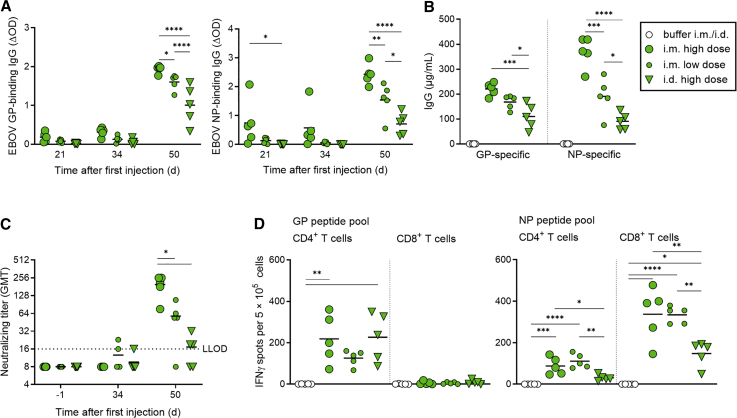
Figure 3.
Immunogenicity of GP + NP using two routes of injection
C57BL/6J IFNAR−/− mice (five per group) were injected intramuscularly (i.m.) or intradermally (i.d.) on days 0 and 35 with LNP-saRNA vaccine candidates in two saRNA doses: high dose (7.5 μg, i.m. and i.d.) or low dose (1.5 μg, i.m. only). The ratio of GP saRNA to NP saRNA was kept at 2:1. Serum samples were collected on days −1, 21, 34, and 50. (A) Seroconversion per group over time. ELISA for EBOV GP and EBOV NP was performed as described in Figure 2. (B) Concentration of GP- and NP-specific IgG on day 50, determined by ELISA as described in Figure 2. Individual IgG concentrations are shown by dots; group mean values are indicated by lines. (C) Neutralizing antibody titers against authentic EBOV are shown by dots; group mean values are indicated by horizontal bars. The dotted line indicates the lower limit of detection (LLOD). (D) Interferon γ (IFNγ) secretion was measured to assess T cell responses in splenocytes isolated on day 50 in all animals of each group, by ELISpot assay as described in Figure 2. Individual spot counts per mice are shown by dots (mean values of triplicate measurements); group mean values are indicated by horizontal lines. Asterisks indicate statistical significance compared with buffer control: ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.