Figure 5. Dual targeting of PDL1 and CTLA4 Restores Macrophage-Mediated Anti-tumor immunity.
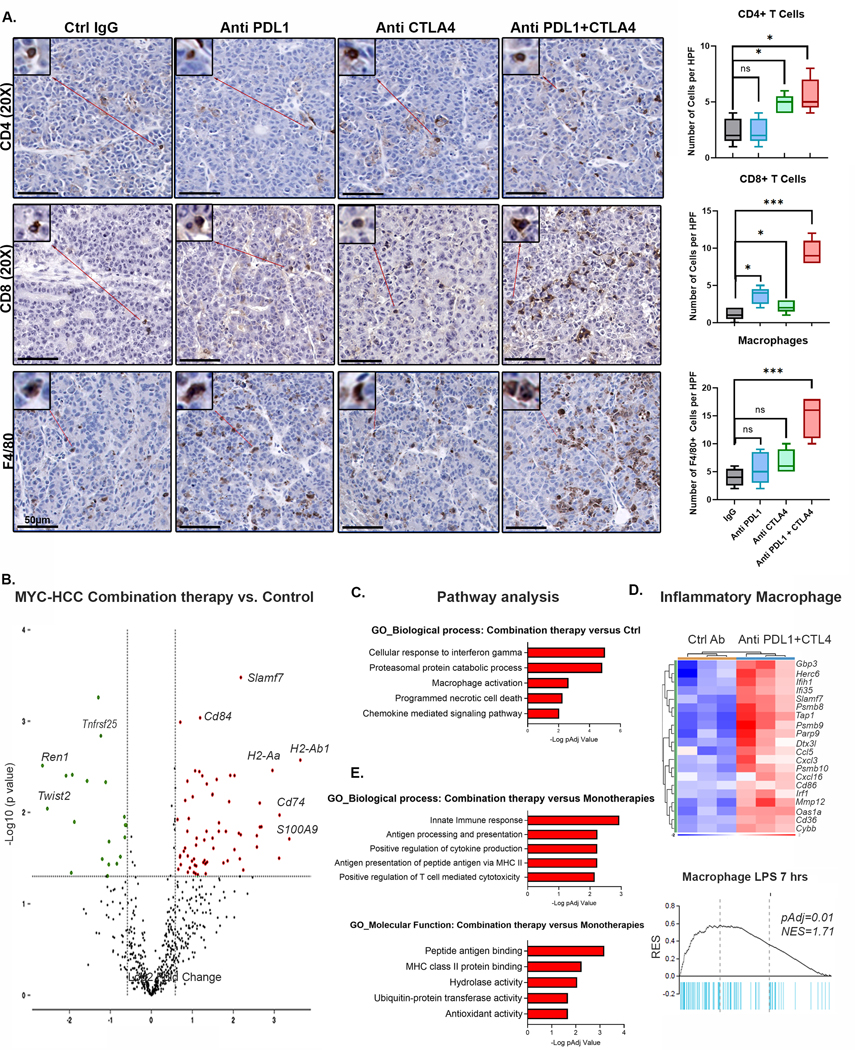
A. Immunohistochemistry for CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and F4/80+ macrophages in MYC-HCC bearing mice treated with IgG control (n=5), PDL1 antibody (n=5), CTLA4 antibody (n=5), or their combination (n=5). Boxplots show quantification of cell counts.
B. Violin plot showing differentially expressed genes between MYC-HCC treated with combination therapy (n=3) versus control IgG (n=3). Macrophage-related genes are upregulated with treatment with anti PDL1+CTLA4.
C. Pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes between MYC-HCC treated with combination therapy (n=3) versus control IgG (n=3).
D. Enrichment of inflammatory signature of macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in tumors treated with combination therapy (n=3) versus control IgG (n=3).
E. Pathways analysis of meta-analysis comparing the transcriptional changes induced by the combination therapy (n=3) to those induced by anti PDL1 (n=3) or CTLA4 monotherapies (n=3).
