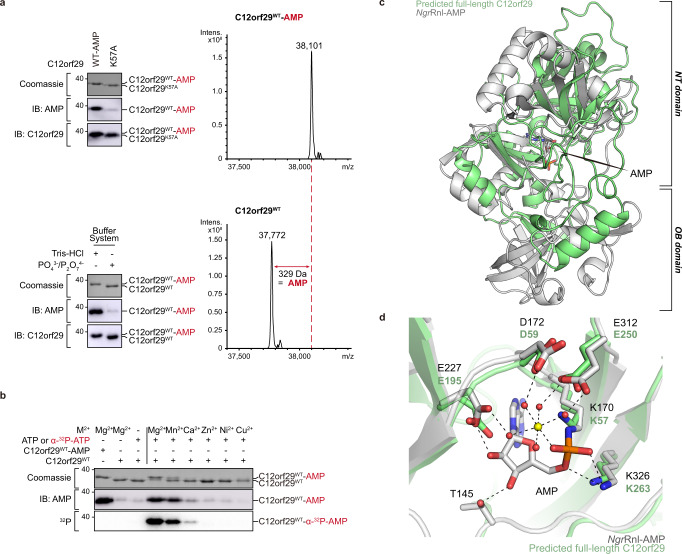
Fig. 2. Auto-AMPylation activity and structural prediction of C12orf29.
a (Top) immunoblotting of C12orf29WT-AMP and C12orf29K57A and LC-MS analysis of C12orf29WT-AMP. C12orf29K57A is deficient in auto-AMPylation activity (representative images of n = 3). Mass spectra indicating a 329 Da increase in mass upon auto-AMPylation of C12orf29WT. C12orf29WT-AMP: calc. 38,100 Da, found 38,101 Da. C12orf29WT: calc. 37,771 Da, found 37,772 Da. (Bottom) preparation of C12orf29WT and C12orf29WT-AMP with different buffer systems (representative images of n = 3). b Divalent metal ion dependency of auto-AMPylation activity of C12orf29WT. c Superimposition of the structure of C12orf29 predicted by AlphaFold (green)31,51 on the structure of NgrRnl-AMP (PDB ID: 5COT, grey). OB, oligonucleotide-binding. NT, nucleotidyltransferase. Structures were superposed in Coot52 using structural equivalent residues identified by the DALI webserver32. d Enlarged view of the catalytic site of NgrRnl-AMP (PDB ID: 5COT, grey) and predicted C12orf29 (green). In the NgrRnl-AMP structure, AMP is covalently attached to the side chain of K170. D172, E227, and E312 bind Mn2+ via water-mediated contacts and K326 contacts the phosphate moiety of AMP. Corresponding residues in the putatively catalytic site of C12orf29 are indicated. Mn2+ and water molecules are depicted as yellow and red spheres, respectively. Atomic contacts are depicted as dashed lines. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.