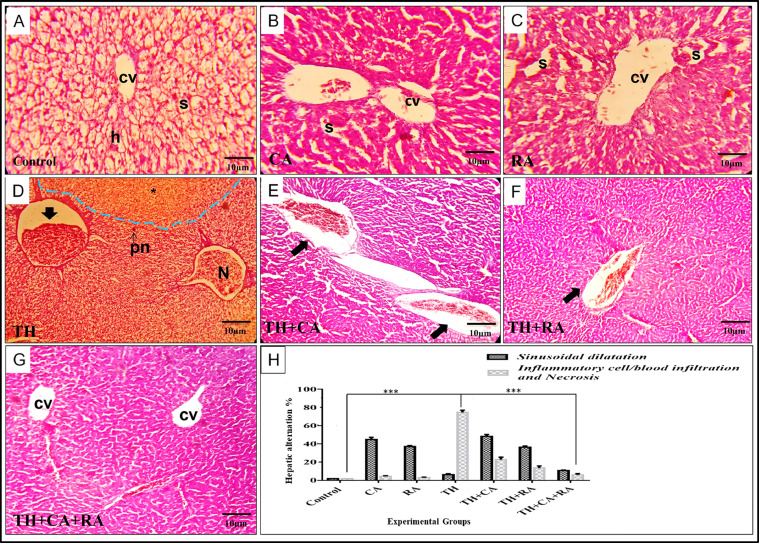
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of liver sections stained with H&E showing the histopathological alternations compared with the control group (A) that exhibited normal hepatic architecture with distinct hepatocyte (h), central vein (cv), and hepatic sinusoidal spaces (s). (B) Liver section of chicoric acid (CA) injected group showing moderate congestion in the central vein (cv) and mild sinusoidal dilation (s). (C) Liver sections of rosmarinic acid (RA) injected group showing moderate dilation and congestion of sinusoidal spaces (s) and congestion of hepatic parenchyma. (D) Liver section of thiacloprid (TH) treated group showing loss of hepatic cord architecture (blue dash line) with small focal necrosis (N), pyknotic nuclei (pn), congested central vein with mild fibrous tissue proliferation, and high inflammatory cells infiltrations (black arrow). (E) Liver section of the co-injected group with TH and CA showing dilation of the sinusoid and marked dilation and congestion of the central vein with small blood cell infiltration. (F) Liver section of the co-injected group of TH and RA showing moderate sinusoidal irregularity appearance and mild central vein dilation with little blood cell infiltration (black arrow). (G) Liver section of the group Co-injected with TH+CA+RA showing the near-normal architecture of liver tissue with distinct hepatocyte strands and normal central vein except for moderate sinusoidal dilation(s). (H) Quantification analysis of sinusoidal dilatation, inflammatory cell aggregation, and necrotic areas. Scale magnification is shown in pictures, and data are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.