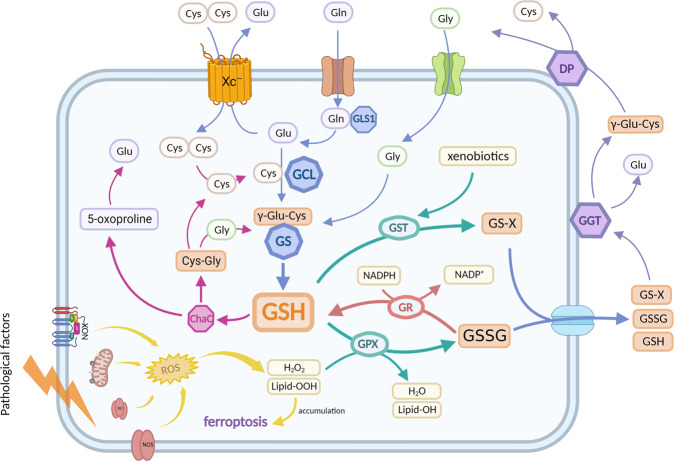
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of intracellular GSH anabolism and function.
The main synthetic pathways of GSH (blue arrows); GSSG is reduced to GSH under the action of GR and NADPH (red arrow); GSH reduces H2O2 (or lipid-OOH) to H2O (or lipid-OH) in the catalysis of GPX, and GSH conjugates with xenobiotics compounds to form GS-X in the catalysis of GST (green arrow); The decomposition process of GSH, GSSG and GS-X after being squeezed out of cells (purple arrows); The decomposition process of intracellular GSH (rosy arrows); ROS are generated from the mitochondrial electron transport chain, nitric oxide synthases (NOS), NADPH oxidases (NOX), and xanthine oxidase (XO) (yellow arrow).