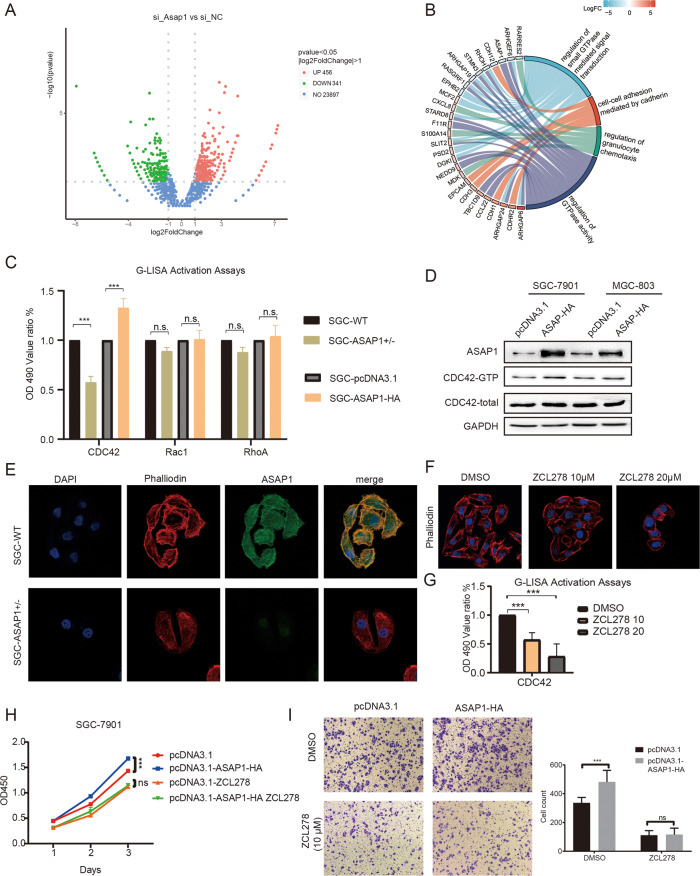
Fig. 5. ASAP1 mediates cytoskeleton assembly by regulating CDC42 expression in GC cells.
A The RNA-seq of ASAP1-depletedGC cell and a volcano plot showing the differential genes. B KEGG pathway analysis showing enrichment of differential gene. C The whole cell lysates were extracted from SGC-7901 cells expressing ASAP1-HA or from ASAP1+/− SG-7901 cells to measure CDC42, RAC1, RALA and RhoA GTPase activity by G-LISA activation assay. D The whole cell lysates prepared from either SGC-7901 or MGC803 cell expressing ASAP1-HA were used for CDC42 activation assay followed by western blotting. E Combined phalloidin staining for F-actin (red) and ASAP1 (green) immunofluorescence. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). In ASAP1+/− SGC-7901 cells, the filamentous pseudopodia disappeared and cytoskeleton depolymerized. F SGC-7901 cells were treated with CDC42 inhibitor ZCL278 and combined phalloidin staining for F-actin (red). The filamentous pseudopodia disappeared and cytoskeleton depolymerized. G SGC-7901 cells were treated with CDC42 inhibitor ZCL278 and the whole cell lysates were extracted to measure CDC42 GTPase activity by G-LISA activation assay. H The proliferation of SGC-7901 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1, SGC-7901 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-ASAP1-HA, SGC-7901 cells treated with ZCL278 or SGC-7901 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-ASAP1-HA followed by treated with ZCL278 was determined by CCK-8. I The migration of various types of cells described in H was determined by Transwell assays.