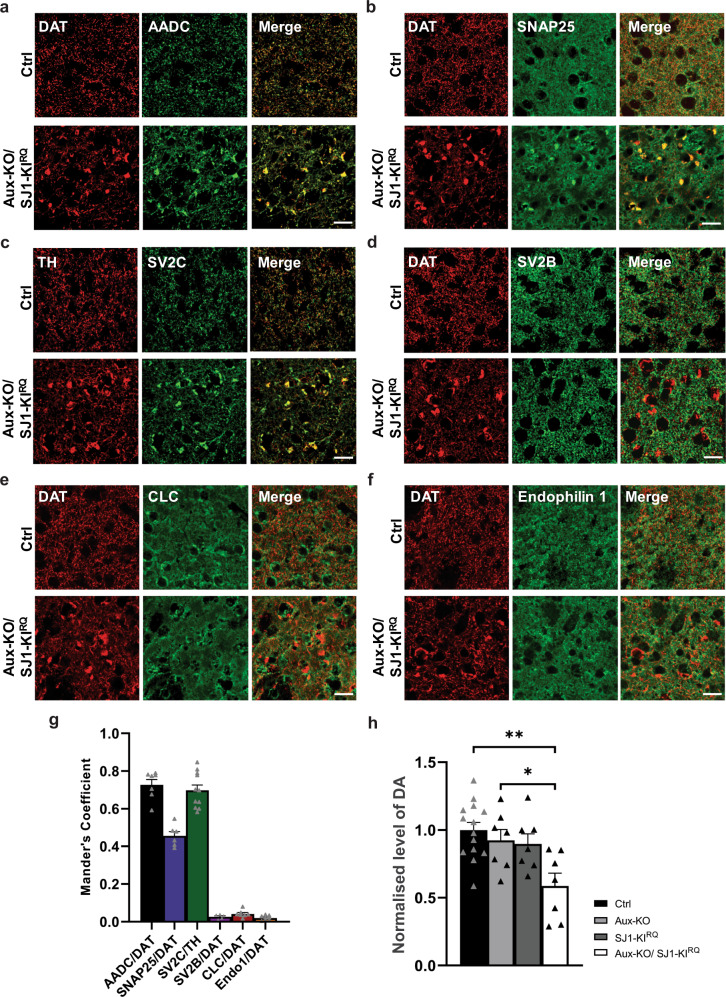
Fig. 6. Accumulation of other proteins with TH/DAT in dystrophic DAergic nerve terminals in 1-month-old Aux-KO/SJ1-KIRQ mice.
a Double staining of DAT with AADC, a DA catabolism enzyme showed colocalization in the striatum of Aux-KO/SJ1-KIRQ mice. Scale bar: 20 µm. b Double staining of DAT with SNAP25, a plasma membrane SNARE protein showed colocalization in the striatum of Aux-KO/SJ1-KIRQ mice. Scale bar: 20 µm. c, d Double staining of SV2C (c) and SV2B (d) reveals that SV2C is specifically accumulated in TH/DAT-positive clusters in the striatum of Aux-KO/SJ1-KIRQ mice, but not its family member SV2B. Scale bar: 20 µm. e, f Double staining of clathrin light chain (e) and endophilin (f) reveals that both endocytic proteins do not colocalize with TH/DAT-positive clusters in the striatum of Aux-KO/SJ1-KIRQ mice. Scale bar: 20 µm. g Mander’s colocalization coefficient shows that AADC and SV2C colocalize the best with DAT/TH clusters, followed by SNAP25. SV2B, CLC and Endo1 do not colocalize with the DAT clusters. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. n = 5–11 random sampling sites. h Aux-KO/SJ1-KIRQ shows 50% reduction in striatal DA levels measured using HPLC. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s test). n = 14 for control and n = 7 for Aux-KO, SJ1-KIRQ and Aux-KO/SJ1-KIRQ, respectively.