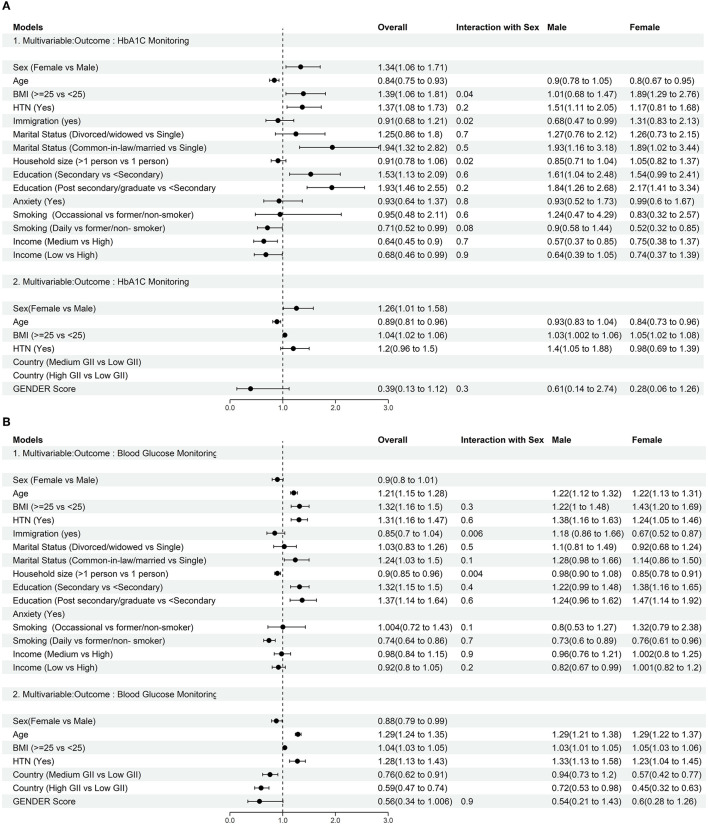
Figure 3.
(A) Forest plot: Assessing role of biological sex and gender variables in care of individuals with diabetes including rate of HbA1c monitoring by health care professional in the past 12 months in Canadian population: Results are presented as Odds Ratio (95% CI). Interaction between sex and gender was assessed via repeated sets of multivariable models including two-way interaction between each gender variable and sex. (B) Forest plot: Assessing role of biological sex and gender variables in care of individuals with diabetes including prevalence of blood glucose monitoring by health care professional in the past 12 months in European population: Results are presented as Odds Ratio (95% CI). Low GII Countries: GII < 0.077: Belgium, Denmark, Finland, Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Slovenia; Medium GII Countries: GII: 0.077–0.1635: Austria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Germany, Greece, France, Spain, Croatia, Ireland, Iceland, Italy, Luxemburg, Poland, Portugal, UK, Lithuania; High GII Countries: GII > 0.1635: Bulgaria, Estonia, Hungary, Malta, Romania, Slovakia, Latvia. Interaction between sex and gender was assessed via repeated sets of multivariable models including two-way interaction between each gender variable and sex.