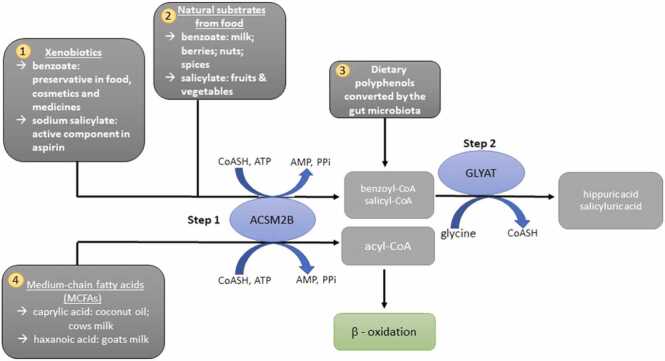
Fig. 1.
An overview of the glycine conjugation pathway and the substrates that it detoxifies. 1 & 2: Benzoate and salicylate (food, medicine and preservatives) are activated to an acyl-CoA by the mitochondrial xenobiotic/medium chain fatty acid: CoA ligase (ACSM2B) and subsequently conjugated to glycine by glycine N-acyltransferase (GLYAT). 3. Gut microorganisms convert dietary polyphenols to benzoyl-CoA, which is a substrate for glycine conjugation. 4. MCFAs, example caprylic acid, are activated by ACSM2B ligase in the liver before entering the mitochondrial beta-oxidation cycle.