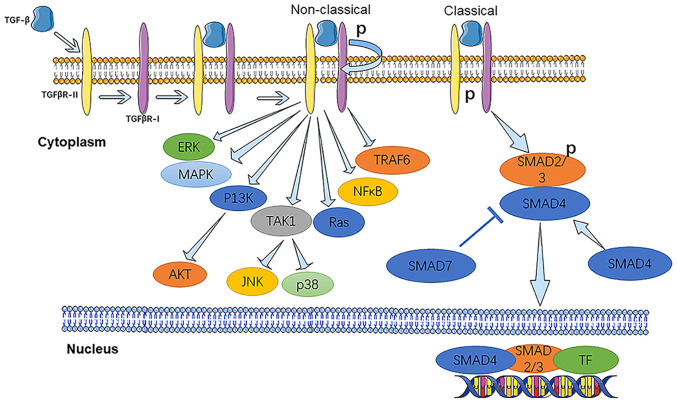
Figure 1.
Classical and non-classical TGF-β signaling pathway. TGF-β ligands bind to TGFβR-II to modify its conformation and mediate its action. TGFβR-II phosphorylates TGFβR-I on specific serine and threonine residues. In the classical pathway, the activated receptor complex phosphorylates receptor-SMADs (SMAD2 or SMAD3), forms a heterogeneous complex with SMAD4 and translocates to the nucleus, where it interacts with transcription factors, coactivators or co-repressors to regulate expression of target genes. In the non-classical pathway, TGF-β activates MAPKs, NFκB, Ras, TRAF6, TAK1/p38/JNK and PI3Ks, leading to biological effects. ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; TAK1, TGF-β-activated kinase 1; TF, transcription factor; TGFβR-I/II, transforming growth factor-β receptor type I/II; TNK1, tyrosine kinase non-receptor 1; TRAF6, TNF receptor-associated factor 4; p, phosphorylated.