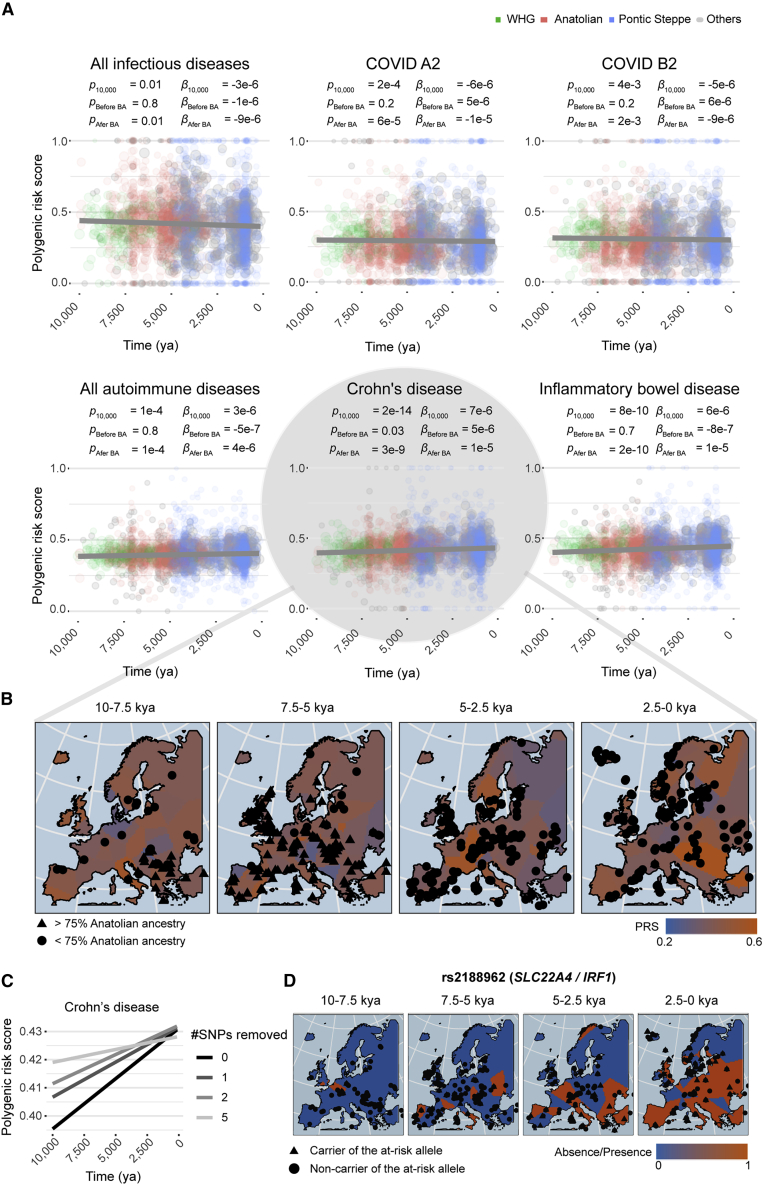
Figure 3.
Resistance to infection and risk of inflammation have increased since the Neolithic period
(A) Polygenic scores for infectious and autoimmune traits as a function of time, over the last 10,000 years. COVID A2 and B2 indicate critical COVID-19 cases versus the general population and hospitalized COVID-19 cases versus the general population, respectively. Dot size scale with the number of SNPs genotyped in the individual. Dark gray lines are the regression lines for a model adjusted for ancestry and geographic location. p values indicate the significance of the regression model, over the last 10 millennia (p), before the Bronze Age (pBefore BA) or since the beginning of the Bronze Age (pAfter BA). Beta values for the regression model considering only samples dating from before (βBefore BA) or after (βAfter BA) the beginning of the Bronze Age are shown. Green, pink, and blue dots indicate individuals with >75% Western hunter-gatherer, Anatolian, or Pontic Steppe ancestry, respectively. Individuals with mixed ancestries are shown in gray.
(B) Polygenic risk score for CD as a function of the geographic location and age of the samples, obtained with the “bleiglas” package of R version 3.6.2. Individuals with >75% Anatolian ancestry are represented by triangles, and the others are represented by circles.
(C) Polygenic risk score for CD as a function of time, after removal of the SNPs most significantly associated with sample age.
(D) Presence or absence of the CD risk allele rs2188962>T as a function of the geographic location and the age of ancient samples.