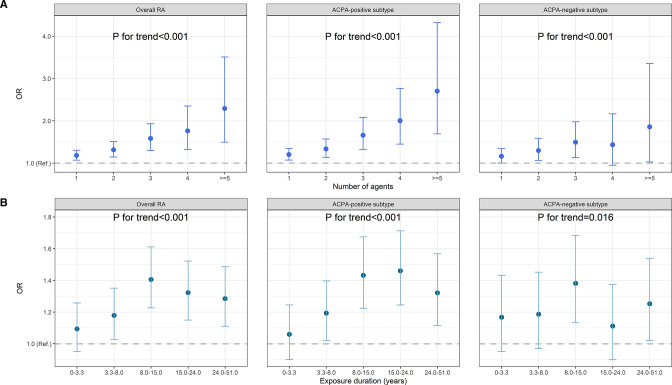
Figure 3.
Exposure–response relationship between occupational inhalable agents and RA. (A) Participants were classified into exposed to 1, 2, 3, 4 or ≥5 agents out of the 16 independent agent collections and compared with non-exposed group (not exposed to any of the 47 agents). (B) Participants were classified into five subsets with exposure durations of 0–3.3, 3.3–8.0, 8.0–1.5, 1.5–24.0, 24.0–51.0 years (to any agents) and compared with non-exposed group (not exposed to any of the 47 agents). Results are shown for overall RA, as well as ACPA-positive and ACPA-negative subtypes. Estimates were adjusted for age, sex, residential area, smoking, alcohol drinking, education and body mass index. ACPA, anticitrullinated protein antibodies; RA, rheumatoid arthritis.