Figure 2.
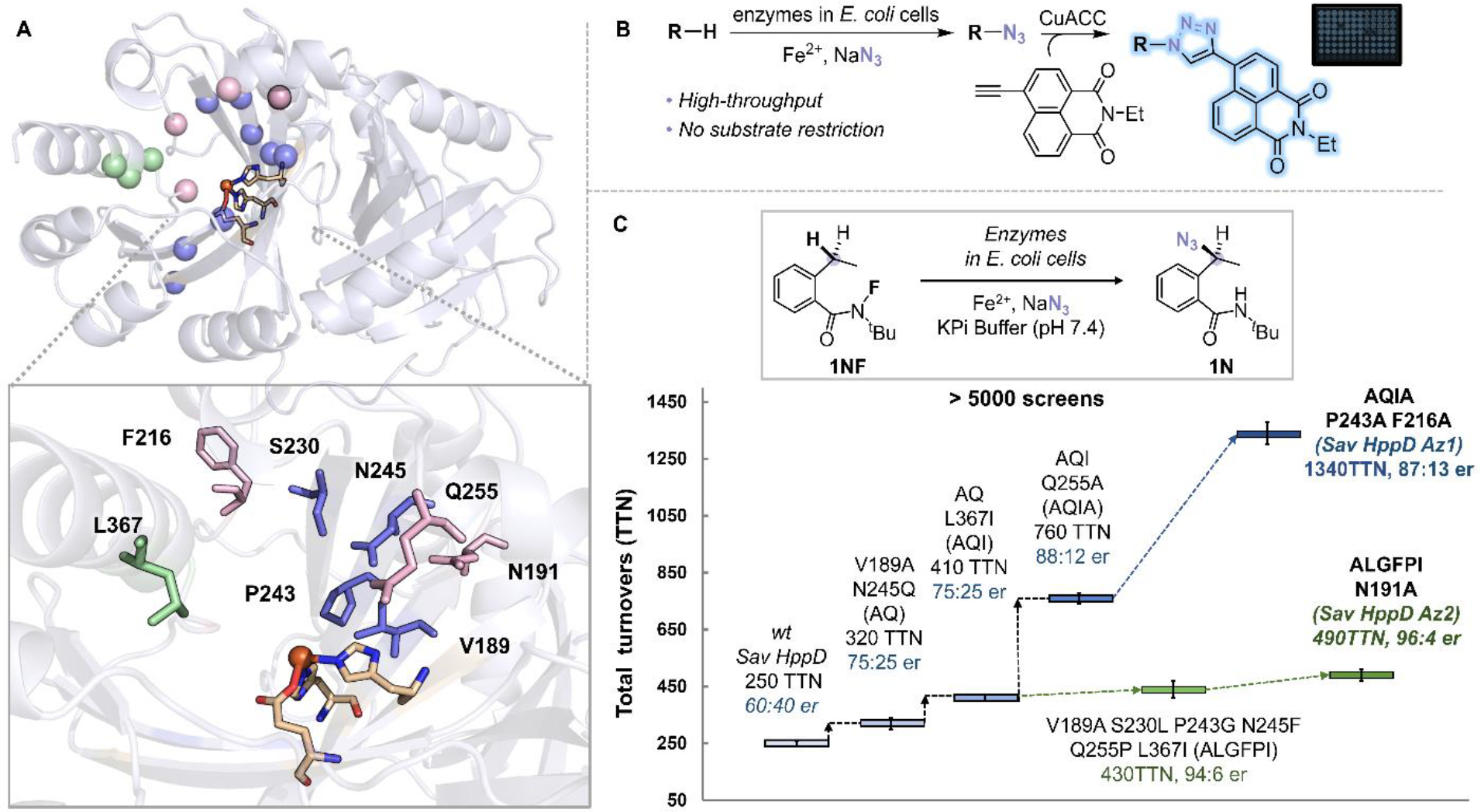
(A) Protein residues selected for mutagenesis (pink: loop residues surounded the active site (N191, F216, Q255, F359), green: residues on the C—terminal α-helix (K361, L367, N363), blue: residues on the β barrel of the C-terminal domain (V189, S230, P243, N245, Q269, Q334, F336, R353) (PDB: 1T47). (B) A high-throughput screening platform for detection of enzymatic azidation products. (C) Representative variants identified during the directed evolution of Sav HppD. Experiments were performed at analytical scale using suspensions of E. coli expressing Sav HppD variants (OD600 = 10), 10 mM substrate 1NF, 25 mM NaN3, 2.5 mM Fe2+ in KPi buffer (pH 7.4) at room temperature under anaerobic conditions for 24 hours (Table S2).
